av Sydney Guyotte för 7 årar sedan
196
Compartments of the Leg
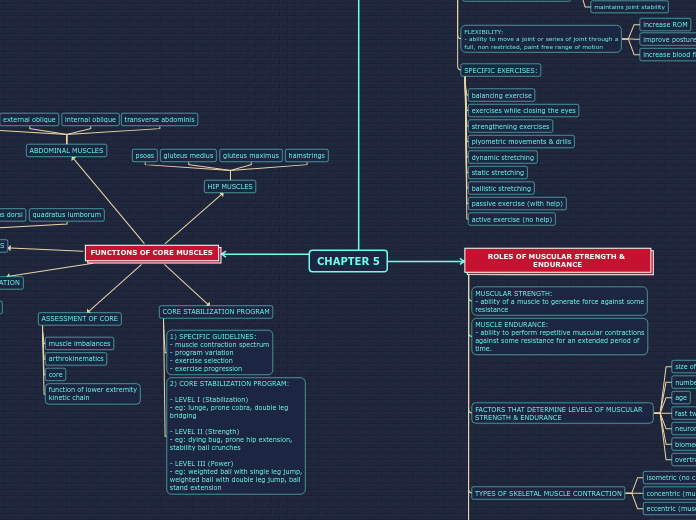
The leg is divided into three compartments: lateral, anterior, and posterior, each containing specific muscles, retinacula, and innervation pathways. The lateral compartment includes the fibularis brevis and longus muscles, held by the superior and inferior retinaculum, and innervated by the superficial fibular nerve.