av Joseph Gonzales för 5 årar sedan
384
Drug Concept Map
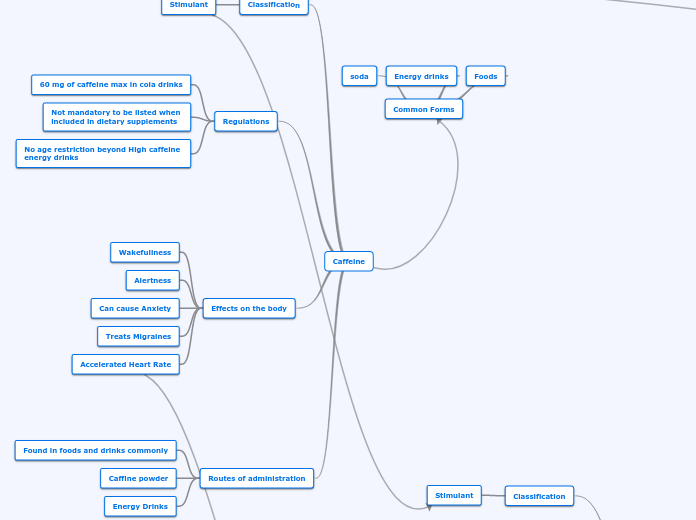
The text outlines the addictive nature and classification of certain substances, particularly focusing on methamphetamine and tobacco. Methamphetamine, a stimulant, mainly affects the brain and central nervous system, leading to severe health concerns such as violent outbursts, paranoia, and insomnia.