Hope you liked it!
Topic flotante
Suppose / Imagine
If the event es referred to a real possibility, a present form is possible
Ex. Suppose you miss the train
Understood conditions: The conditional part of this kind of sentences is often understood but not stated
Ex. Suppose your crush declared his love for you
Ex.Imagine you won the contest!
As if / As though
Can be real and unreal
The more colloquial like is, it doesn't requiere the verb form change
Ex. You look as you've just seen a ghost (formal)
Ex. You look like you've just seen a ghost (informal)
The verb form depends on whether the situation is real or not
Ex. You look as if you've seen a ghost (Unreal, he's just scared because something bad happened)
Ex. You look as if you're having a headache (true, he is having a headache)
I'd rather / I'd prefer
Followed by a clause
I'd prefer can be used in the same way, but in this kind of sentence has an object it
However, I'd prefer is not followed by an unreal verb form in other situations
Ex. I'd prefer it if you didn't go
I'd rather and I'd sooner are used with normal verb forms when comparing nouns and phrases
Ex. I'd rather study Music than Literature
I'd rather is followed by past verb forms (same as in wishes about the present), and it expresses preference about actions
Ex. I'd rather you didn't smoke in here
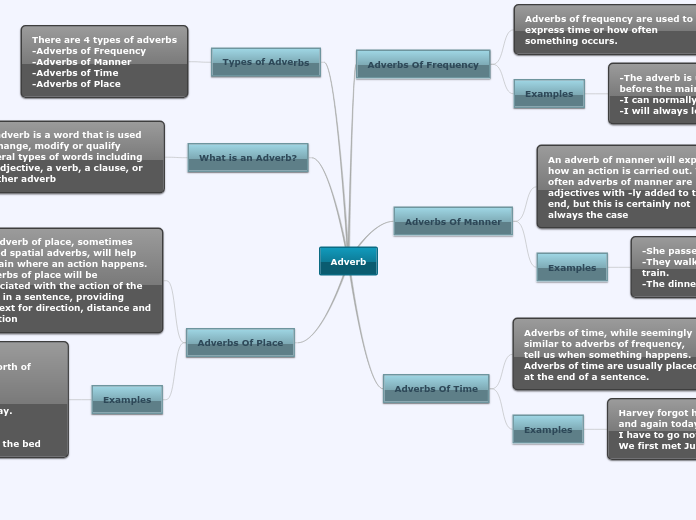
Wishes
Hope
This expresses wishes about simple future events
Ex. I hope it doesn't rain tomorrow
Past time
As with present wishes, the verb form after wish is one stage further back in the past. These are wishes referring to a past event that cannot be changed
Ex. I wish I hadn't eaten so much
This use of wish is common after If only to express regrets
Would
Its use often describes an annoying habit
Ex. I wish you wouldn't be so noisy
Used when the speaker wants somebody or something else to change
Ex. I wish he would change his mind and see me like something else
Present/future time
Here's another past form
Ex. I wish you weren't leaving (You're leaving now)
These are wishes where we want to change a present/future state
Ex. I wish I had a car (I don't have one now)
It's time, it's high time
These are followed by past simple or continuous, though the time referred to is unreal
It's high time we were heading home now
It's time I went home now
Unreal time
Unreal situations
Also used in subordinate clauses after wish and suppose
I wish you were here (You are not here)
I wish the journey were over (It's not over)
If I were you, I would apply right now (I am not you)
Used in conditional and concessive clauses
Operative Subjunctive
Used in fixed expressions
God save the Queen
Be that as it may
If I have to pretend that you no longer exist, so be it.
A toast now: long live the bride and groom.
This structure may be unsual and difficult at first sight, but once you understand it
The teacher demanded that we do our homework during class
This use is more characteristic of AmE
Mandative subjunctive
Used in That-clauses after an expression of such notions as
Intentions
Proposal
Recommendations
Demands
The Subjunctive mood expresses wishes, conditions contrary to fact, and requests and commands
Past subjunctive
Hypothetical meaning
Present subjunctive
There are two main uses
Subjunctive Mood
Explained in detail
Compounds and idioms
Idioms are a group of words in a fixed expression that cannot be guessed
Here are some examples
Compounds are units of meaning formed with two or more words, separated for a hyphen or written as one
Here's a catchy and funny way to explain this topic
They can be guessed by knowing the meaning of the individual words
Types of collocations
Adverb + Adjective (Happily married)
Verb + Adverb (Whisper softly)
Verb + Prep (Filled with anger)
Noun + Noun (A sense of pride)
Noun + Verb (The company has grown)
Verb + Noun (Make a fuss)
Adjective + Noun (Bright color)
COLLOCATIONS
Pair or group of words that are often together
Some are strong and fixed
Some combinations just sound wrong for L1 people
They help improve style in writing
They give us an alternative way to say something
They help us sound natural
They generally have words with more tan one sentence function
I don't like Peter / doing / that (Subject + verb + D.O)
They can be expanded into a full clause with a finite verb
While running for the bus, I slipped on the ice = While I was running for the bus, I slipped on the ice.
But there are two reasons for not doing that
Phrases and Clauses
A phrase does not have a subject and a verb, whereas a clause does
For this reason, non-finite and verbless clauses are treated as phrases in traditional grammar
When there is no expressed subject in a non-finite or verbless clause, the implied subject is the subject of the verb in the main clause
Ex. I don't want to do that (the implied subject of 'to do' is 'I')
Dangling Participles
Participle in a non-finite clause whose implied and unexpressed subject is not the same as the subject of the verb in the main clause
Ex. I don't want to do that (unexpressed subject)
Ex. I don't want you to do that (expressed subject)
INDIRECT COMMANDS
I told her not to do that (indirect command)
'Don't do that,' I said to her (direct command)
Non-finite clauses are used to form
Both non-finite and verbless clause, can function as a noun and adverbial clauses. In addition, they have the same function in sentences as subordinate clauses
Ex. While in town, I met your mum (verbless clause as adjunct, saying when)
Ex. Painting the kitchen will take ages (non-finite clause as subject)
Verbless Clause
This kind of clause has no verb in it
Ex. Now much better, she could smile.
EX. Come next week if possible
Non-finite clause
There are four types
Gerund
Ex. When cooking the meal, I cut my finger.
Verbal noun
Ex. I keep on hearing funny noises.
Participle
Ex. Once made, the decisión is final.
Infinitive
Ex. To graduate, I need to study hard.
Finite and non-finite verbs & clauses
Non-finite verbs don't indicate tense
Finite verbs indicate tense
GRAMMAR IV
Topic principal