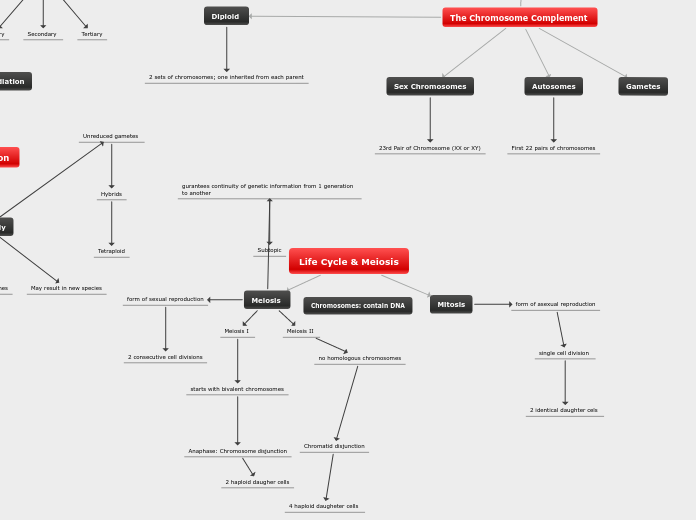
The Chromosome Complement
Chromosomal Nondisjunction
Monosomics
Trisomics
Down Syndrome
Diploid
2 sets of chromosomes; one inherited from each parent
Gametes
Autosomes
First 22 pairs of chromosomes
Sex Chromosomes
23rd Pair of Chromosome (XX or XY)
Energy Flow in Ecosystems
Living Organisms
Detritivores
Consumers
Tertiary
Secondary
Primary
Produceers
productivity
Primary Prodcutivity
Net Primary Productivity=Gross primary productivity - plant respiration
Ecosystem
group of plants & animals interconncected by energy and mineral flow
Speciation
Adaptive Radiation
development of new species from common ancestor due to adaptations to different environments
Polyploidy
Examples: Tragopogon & Triticum
Unreduced gametes
Hybrids
Tetraploid
May result in new species
State of having more than 2 sets of chromosomes
Population Regulation
Annual Growth Rate
BR - DR / 10
Environmental Resistance
Factors that oppose population growth
Adverse Weather Conditions
Emmigration
Insufficient food
Predations & Pathogens
Diseases
Biotic Potetial
Factors that promote population growth
defense mechanisms
ability to withstand adverse conditions
Rate of reproduction
Carrying Capacity
the maximum individuals of a population that an environment's resources can support
Chromosomes: contain DNA
Species Interactions
Competition
Predation
Resource Partitioning
slight variations in niche that allow species to coexist
Mutualism
limits geographical distribution
soil type
predators and pathogens
competition
precipitaton
temperature
Life Cycle & Meiosis
Mitosis
form of asexual reproduction
single cell division
2 identical daughter cels
Meiosis
gurantees continuity of genetic information from 1 generation to another
Subtopic
Meiosis II
no homologous chromosomes
Chromatid disjunction
4 haploid daugheter cells
Meiosis I
starts with bivalent chromosomes
Anaphase: Chromosome disjunction
2 haploid daugher cells
form of sexual reproduction
2 consecutive cell divisions