Learning Design A
Learning Theories - relevance in specific education eco-system
Adult Learning - Training of Teachers (Professional Development)
- Learning Theories are useful to look at how people learn
- Key features, learning manifestation and teaching methods relating to each can be analysed for appropriatness and relevance in designing learning for teachers
Eco-system: Teacher Professional Development
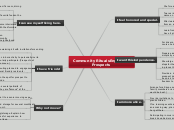
This mind map represents the thinking about Learning Design for Teacher Professional Development.
It is based on an individual mind map on Learning Theories as well as a group-constructed mind map on the same topic.
It uses Learning Theories as a basis for looking at criteria to consider when doing Learning Design in this educatinal eco-system.
The larning design considerations are displayed on the left hand side of the mind map.
All concepts that are related, similar or connected are linked (which may seem chaotic at first, but by following the links the connection should become clear).
Learning Design for Teacher Professional Development needs to be Learner-Centered, Knowledge-Centered, Assessment-Centered and Community-Centered. This corresponds with key features of most of the major Learning Theories. This perspective is based on the theory that people learn better when they are motivated, ready, the experience or outcomes are relevant, when it involves other members of their community, when it is collaborative, when there is feedback on progress and when it builds on existing knowledge.
This suggests certain teaching methods that can be included in the Learning Design like:
- Problem-based Learning
- Project-based Learning
- Cooperative Learning
- Inquiry-based Learning
- Mentoring
- Modelling
It also suggests that 21st Century Learning is relevant for today's teacher, that higher order thinking skills need to be involved during learning adn that variety must be included to accomodate differences among the learning group.
Variety
Assessment methods
Formative
Online
Self
Project
Activities
Information
Find in rela world / experience
Peer
Internet
Higher Order Skills
Application
Synthesize
Analyse
Critical thinking
21st Learning Skills
Lifelong Learning
Critical Thinking
Collaboration
Design
Creativity
Knowledge-Centered
Mentoring
Modeling
Community-Centered
Peer netowrks
Communities of Practice
Real world problems
Exsiting knolwledge
Case based
Project based
Problem based
Inquiry-based
Learning Design
Learning Desing
LD needs to take into account different theories of how people learn.
Blooms Taxonomy
Higher order:
Lower order
Learning Theories
Cognitivism
Inner mental activities (individual)
Gagne
Retrieve and apply knowledge
Problem-soving
Higher order thinking / skills
Active Learning
Discovery Learning
Expository Learning
Biological stages of human development
Cognitive Development
Transformative Learning
Self directed Learning
Social Cognitivism: learning by observing others
Bandura
mentoring
modelling
Leanring manifestation:
Self-directed learning
Socialisation
Connectivism
21s Century Learning
Techo-Constructivist
Senge
Checkland
Bertalanffy
Harasim
Prensky
Drago
Gamification
Inquiry based Learning
Multimedia
Social Media
Emotion
Cooperative Learning
Guided exploration
Adaptive Expertise
Life Long Learning
Apply knowledge
Higer order skills /thinking
Peer networks and Internet-enabled learning
Downes
Siemens
Guided
Real-world problems
Action Learning
Team
Communication
Experiantial Learning
Behaviourism
Knowledge Transmission
Overview
Staats
Skinner
Watson
Pavlov
Train
Drill
Practice
Instruct
Text
Lecture
Video
Key features
Teacher-Centric
Direct instruction
Task-based
Lower Order Skills
Stimulus + Response
Skills
Accountability
Performance
Behaviour
Social Constructivism
Knowledge constructed through social interaction
Ovewview
Kolb
lave
Bronfenbrenner
Bruner
Dewey
Vygotsky
Piaget
Teaching methods
Problem-solving
Inquiry based learning
Cooperative learning
Case-based learning
Project-based learning
Key Features
Learner-Centered
Meta-gognition
Situated Cognition
Authentic Learning
Ill-defined problems
Social Context
Learning manifestation:
Cooperative
Reflective
Transformative
Siutational
Experiantial