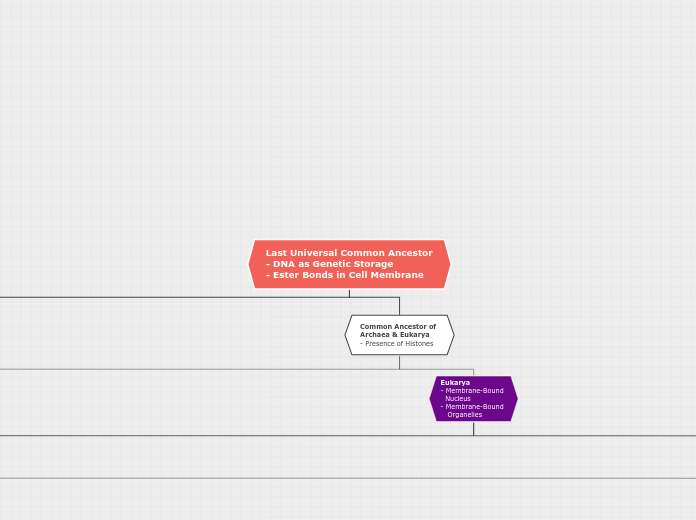
Last Universal Common Ancestor
- DNA as Genetic Storage
- Ester Bonds in Cell Membrane
Common Ancestor of
Archaea & Eukarya
- Presence of Histones
Eukarya
- Membrane-Bound
Nucleus
- Membrane-Bound
Organelles
S A R
Rhizeria (Amoebas With
Thread-Like Pseudopodia)
Radiolaria
Foraminifera
Common Ancestor
(Secondary Plastids)
Stramenopile
(Heterokonts)
-Tripartite Flagellar
Hairs, smooth and hairy
flagella)
Oomecytes
(Water Moulds)
Brown Algae
Giant Kelp
(Macrocystic pyrifera
brown algae)
Diatoms
Alveolata (Membranous
Vesicles on Cell Wall)
Dinoflagellate
Unikonta/
Amorphea
Opisthokonta
(fungi, animals)
-Multicellularity
-Absorptive
Heterotrophy
Holozoa
Common Ancestor
Of Animals and
Choanoflagellates
-Mobility
Animals (Metazoa)
770 MYA
-Gametic
Life Cycle
-MultiCellularity
-Mobility
Parazoa
Porifera
(Basal Taxa)
-No Tissues
-No Symmetry
-Choanocytes
-Specialized Tissue
Giant Barrel Sponge
(Xestospongia muta)
Eumetazoa
-Tissues
-680 MYA
Ctenophora
(Comb Jellies)
-Arguments about
diploblasty or
triploblasty
Common Ancestor
of Bilateria and
Cnidaria
Radiata
Cnidaria (jellyfish,
corals, sea anemones,
and hydra)
-Diploblasty
-Radial Symmetry
-Cnidocytes
Common Ancestor
of Scyphozoa and
Hydrozoa
Hydrozoa
-Alternate between
Medusa and Polyp
Stages
Pennaria disticha
Scyphozoa
-Dominant
Medusa Stage
Moon Jelly
(Aurelia aurita)
Anthozoa
-Dominant
Polyp Stage
Elkhorn coral
(Acropora palmata)
Bilateria
-670 MYA
-Bilateral Symmetry
-Triploblasty
-Cephalization (except
some mollusca, Echinoderms
Acoela
-Early Cephalization
-Early Triploblasty
Common Ancestor of
Deuterostomia and
Protostomes
-Triploblasty
Deuterostomia
-Blastopore
becomes the anus
-Radial and
indeterminate cleavage
Chordata
-Notochord, Hollow
Dorsal Nerve
Cord, Pharyngeal Slits,
Post Anal Tail
Common Ancestor of
Urochordata (tunicates)
and Vertebrates
Vertebrates
Common Ancestor of
Agnathans
Gnathostomes, Osteichthyans,
Lobe Fish,
Tetrapods, , Amniotes.
-Vertebrae
-Vertebral Column
-Cranium
-Endoskeleton
-Complex Internal Organs
Common Ancestor of
Gnathostomes,
Osteichthyans,
Lobe-Fins,
Tetrapods, Amniotes
-Jaws, Mineralized
Skeleton
-Paired Fins
Common Ancestor of
Osteichthyans, Lobe-Fins,
Tetrapods, Amniotes
-Lungs or Lung Derivatives
-Swim Bladder
-Bony Skeleton
-Opperculum
Common Ancestor of
Lobe-Fins, Tetrapods,
Amniotes
-Lobed Fins
Common Ancestor of
Lobe-Fins, Tetrapods,
Amniotes
Common Ancestor
of Tetrapods and
Amniotes
-Limbs with Digits
-3 and 4 Chambered Hearts
-Double Circulation
Common Ancestor
of Amniotes
-Amniotic Egg
Synapsids
Mammalia
(Mammals)
-Milk
-Endothermy
-Hair
-4 Chamber Heart
Monotreme
-Platypus lay eggs
American Black Bear
(Ursus americanus)
Diapsids
Reptilia
(Turtles, snakes,
Crocodiles, birds)
-3 or 4 Chamber Hearts
Common Ancestor
Of Turtles and
Archosaurs
Turtles
Green Sea Turtle
(Chelonia mydas)
Archosaurs
Crocodilians
-4 Chambered Hearts
American alligator
(Alligator mississippiensis)
Common Ancestor of
Pterosaurs, Dinosaurs,
and Saurischians
Pterosaurs
Birds
-Endothermy
-4 Chamber Hearts
Roseate spoonbill
(Platalea ajaja)
Lapidosaurs
(Snakes and Lizards)
Green anole
(Anolis carolinensis)
Amphibia
(Frogs, salamanders)
Red Eyed Tree Frog
(Agalychnis callidryas)
Dipnoi
(Lungfishes)
Leopard lungfish
(Protopterus aethiopicus)
Actinistia
(Coelacanths,
Lobbed-Fin Fishes)
Coelacanth
(Latimeria chalumnae)
Actinopterygii
(Ray-Finned Fishes)
Blue Tang "Dory"
(Paracanthurus hepatus)
Chondrichthyes
(Sharks, Rays,
Chimaeras)
-Cartilaginous
Skeleton
Great White Shark
(Carcharodon carcharias)
Agnathans (Lamphreys
Hagfish)
Cyclostomes
-No Jaws
-No Paired Lateral Fins
-Reduced Vertebrae
-Cartilage Skeleton
Petromyzontida
(Lampreys)
Myxini
(Hagfish)
Pacific hagfish
(Eptatretus stoutii)
Tunicata/ Urochordate
-Reproduce by Budding
-Colonial or Solitary
-Benthic and Pelagic
-Complete Digestive System
-Heart and Stomach
Sea Squirt (Polycarpa aurata)
Cephalochordates
-Lancelets
-Has the 5
Synamorphies
Branchiostoma lanceolatum
Ambulacraria
Echinodermata (Starfish,
Sea Urchin, Cucumbers)
-Water Vascular System
(exception to bilateral
symmetry as adults)
-Pentaradial Symmetry
-Spiny Skin
Common Ancestor
of Asteroidea
and Ophiuroidea
Ophiuroidea
-Brittle Stars
-Tube Feet High Reduced
-Long Arms for Locomotion
Serpent Star
(Ophiura ophiura)
Asteroidea
-Sea Stars
-Water Tube
Feet Locomotion
Giant Sea Star
(Pisaster giganteus)
Common Ancestor
of Echinoidea and
Holothuroidea
Holothuroidea
-Sea Cucumber
-Elongated
-Lack Spine
-Endoskeleton Reduced
- Tiny Rows of Tube Feet
-Filter Feed
California sea cucumber
(Apostichopus californicus
Echinoidea
-Sea Urchin
and Sand Dollar
-No Arms
-Spine and Tube Feet
-Herbivores
Hemichordata
Protostomes
-Blastopore
becomes the mouth
-Spiral and determinate
Cleavage
Lophotrochozoa
-Trochophore Larvae
and Lophophore
Brachiopoda
-Like a snail w/ a shell
-Lophophore inside shell
used to filter feed
Rotifer
-Pseudocoelemate
-Wheel-Like Cilliated
Corona used to move food
towards mouth for feeding
Ectoprocta
Common Ancestor
of Mollusca and
Annelida
Annelida
(Segmented Worms)
-Trochophore Larvae
Errantia
-Long Setae
-Mobile Predators
Sedentaria
-Reduced Setae
-Sedentary
Common Earthworm
(Lumbricus terrestris)
Mollusca
(Gastropods,
cephalopods,
bivalvia)
-Soft Body sometimes
with Shell Secreted from Mantle
-Trochophore Larvae
Polyplacophora
Chitons
Strong foot attach
to Rocks
Common Ancestor
of Gastropoda and
Cephalopoda
Cephalopoda
-Squid, Octopus,
Cuttlefish, Nautilus
-Shell reduced
-Cephalization
-Head - Foot (tentacle)
-Closed Circulatory System
Humboldt squid
(Dosidicus gigas)
Gastropoda
-Snails and
Slugs
-Radula to feed
-Filter Feeder
-Gill for feeding and
gas Exchange
Golden Apple Snail
(Pomacea canaliculata)
Bivalvia
-2 Valves hinged
dorsally
-Filter Feeder
-No Head
Soft Shell Clam
(Mya arenaria)
Platyhelminthes
(Flatworms)
-Lophophore
Common Ancestor
of Trematodes and
Cestoda
Cestoda
-Tapeworms
-Parasitic
Pork Tapeworm
(Taenia solium)
Trematodes
-Parasites
Rhabditophorans
-Free Living
-Predators n Scavengers
Sheep Liver Fluke
(Fasciola hepatica)
Pseudobiceros sp
Ecdysozoa
-Ecdysis
Arthropoda
(Crustaceans, Insects,
Spiders)
-80% of All Animals
-Hinged Exoskeleton
Common Ancestor
of Hexapoda and
Crustacea
Crustacea
-Cephalization
-Gills
Chesapeake Blue Crab
(Callinectes sapidus)
Hexapoda
-Insects
-6 Legs
-Three Segments
-Trachae and Air Sacs
Monarch butterfly
(Danaus plexippus)
Chelicerata
-8 Legs
-Spiders, Scorpions,
Mites, Ticks
-Book Lungs
-Two Segments
Southern Black Widow
(Latrodectus mactans)
Nematoda
(Round Worms)
Roundworm
(Caenorhabditis
elegans)
Choanoflagellates
(Desmarella moniliformis)
-Heterotrophic
-Characterized by collar
-Flagellated
Holomycota
Common Ancestor of
Nucleariids and
Fonticula alba
Nucleariids
-Filose pseudopodia
-Mitochondria
-Heterotrophic
Nuclearia thermophila
Fungi
-Zygotic Life Cycle
- Chitin Cell
Wall
-Multicellularity
Basidiomycota
Fly Agaric
(Amanita muscaria)
Black Bread Mold
(Rhizopus stolonifer)
Amoebazoa
(Lobe or Tube
Shaped
Pseudopodia)
Slime Molds
Excavata
(unicellular, heterotrophic
flagellates, feeding groove)
Euglenoids (spiral
or crystalline rod
inside flagella)
Archaeplastida (red algae,
green algae, land plants)
-Primary Plastids
Common Ancestor of Chlorophytes,
Charophytes, and Land Plants
Common Ancestor of
Charophytes and Land Plants
Common Ancestor of
Land Plants
-Sporic Life Cycle
-Presence
of Embryo
-Desiccation Resistant
Spores
-Apical Meristems
-Gametangia
-Sporangia
Common Ancestor
Common Ancestor of
Seedless Vascular Plants
-Lignin
-Xylem and Phloem
-Dominant Sporophyte Generation
-Thick Waxy
Cuticle
-Stomata
Common Ancestor of
Monilophytes, Gymnosperms,
and Angiosperms
-Megaphylls
-Ovules
-Pollen
-Seeds
-Heterospory
-Wood
Gymnosperms
Scott's Pine
(Pinus sylvertris)
Bald Cypress
(Taxodium distichum)
Angiosperms
-Fruit
-Endosperm
-Ovaries
-Flowers
White Water Lily
(Nymphae alba)
Southern Magnolia
(Magnolia grandiflora)
Monilophytes
-megaphylls
Easter Marsh Fern
(Thelypteris palustris)
Lycophytes
-microphylls
Fan Clubmoss
(Diphasiastrum
digitatum)
Hornworts
Field Hornwort
(Anthoceros agretis)
Mosses
Woolly Feather Moss
(Tomentypnum nitens)
Liverworts
Common Liverwort
(Marchantia polymorpha)
Charophytes
Braun's Stonewort
(Chara Braunii)
Chlorophytes
Rhodophytes
(Red Algae, Photosynthetic
Pigment)
Archaea
-Ether Bonds in
Cell Membranes
Methanobrevibacter smithii
Bacteria
-Presence of
Peptidoglycan in
Cell Wall
Escherichia coli