av Anne San för 4 årar sedan
752
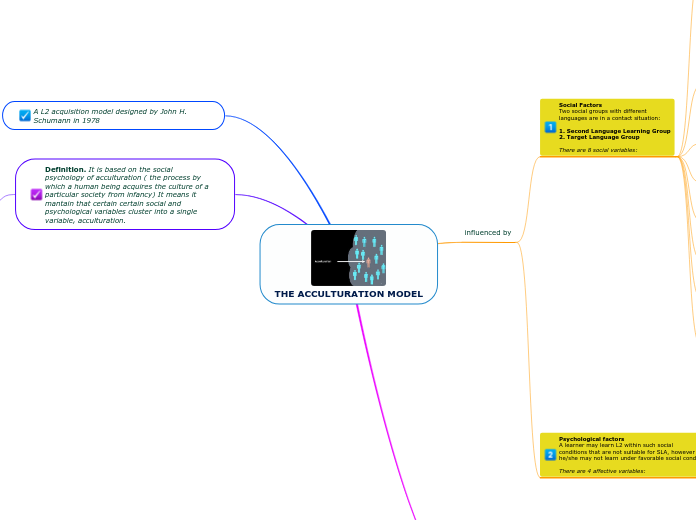
THE ACCULTURATION MODEL
Communication Accommodation Theory (CAT) investigates how individuals adjust their speech patterns to either converge with or diverge from their interlocutors, influenced by factors such as age, gender, race, and cultural background.