Validation
Practice
Declaration
Profession
Foundation
Conviction
“Iman has over sixty branches (parts): the highest of which is the belief that nothing deserves to be worshipped except Allah and the lowest of which is the removal from the way of that which might cause harm to anyone. And modesty (haya’ الحياء) is a branch of it.” (hadith)
“A believer by virtue of his good morals may attain the status of one who fasts (voluntary fast) regularly and performs prayer at night”. (hadith)
When the Prophet (saw) was asked: Whom Allah likes most amongst His subjects? He replied: “The one who possesses superior moral qualities”. (hadith)
“Courtesy and good morality melt the sins just like water melts the ice. And immorality spoils good deeds as vinegar spoils honey.” (hadith)
“None of you will have faith (will be a true believer) till he wishes for his (Muslim) brother what he likes for himself.” (hadith)
“The most perfect believer in faith is the one who is best in moral character. ..” (al-Tirmidhi)
“…Take alms of their wealth, so that it may purify and sanctify them. (9: 103)
“O you who believe! Fasting was made compulsory for you, as it was made compulsory for those who preceded you, so that you may become righteous.” (2: 183)
“…whoever determines the performance of the pilgrimage therein, there shall be no lewdness (depravity) nor abuse nor angry conversation on the pilgrimage(2: 197).
“…And establish regular prayer; for prayer restrains from indecency and evil” (29: 45)
Moral
Training
Enjoining
& Forbidding
As a means
Prophet’s
Excellent example
Performing an
Obligatory acts
Divine religion
As the source
Reform of Self
Practical
Training
Social change
& Social
Training
Establishment
Of adalah
Striving and
Searching
The truth
Enjoining
& Forbidding
Setting up
As a model
Companionship
Of Good
Academic
Attaining
Knowledge and
Doing virtues
Lives of
Sahaba &
Salihin
Improving
Relationship
With Allah
Motivation &
Determination
Love of the
Prophet
Thought for
Life after
death
Sensitivity &
consciousness
Reciting and
Understanding
The Quran
To be closed
To Allah
Purifying
The soul, faith
& actions
Obeying/
Practicing
Life of the
prophet
Following
Lessons from
Pious people
Observing
Salat al-Nawafel
& Fasting
THE CONCEPTS OF ETHICS
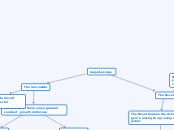
STRUCTURE OF ISLAMIC ETHICS
Practical training
Moral training
Academic / Intellectual training
Spiritual training
FIELD OF ETHICS
Applied
Example
Cooperation
Justice
Right to life
Obedience to parents
Application of normative theories to practical moral
problem
issues
Metaethics
Systematically studies the meanings
judgments
ethical terms
Normative
Seek to set
standards
norms
IMPORTANT OF ETHICS
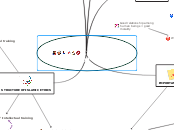
Validation and authentication of Iman
Definition of Iman
The level of faith (iman) is proportional to the level of morals
Good morals are conditions of validity of Iman
Benefits
Spiritual
Good morals = voluntary worship
The dearest one to Allah
Good morals eliminate sins
Social
Wining hearts of people
Building good reputation
Strong & peaceful family life
harmonious society
Good leadership
The spirit of Islam
What is Islam?
Good relationship with Allah in its spiritual sense
Good relationship among human beings = good morality
pure worship (‘ibadat) is for moral purposes
al-Zakah
al-Salah
al-Siyam
al-Hajj
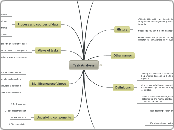
ETHICS IN ISLAM
Al-akhlak/ethics
Al-Ghazali
character is an established state (of the soul) from which actions proceed easily without any need for reflection or deliberation
“the study of certain religious beliefs (i‘tiqadat) and of rightness and wrongness of action for the purpose of practice and not for the sake of mere knowledge.”
science of practical religion (‘ilm al-mu‘amalah).
the science of the path of the Hereafter (ilm tariq al-akhirah) or path trodden by the prophets and righteous ancestors (al-Salaf al-Salih).
according to Abdul Qadir al-Jurjani
a deep state of the self produces acts, behavior with ease with no need of sophisticate thinking and reflection
Known as
'ilm al-akhlāq
from word khuluq
the spiritual constitution of man
‘inner disposition’ of the soul
character
branch of knowledge
studies akhlāq (morals)
science of morality
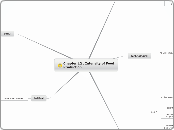
DEFINITION
Morality
Latin :‘moralis’ ‘mores’, custom, the traditional norm of a people
Ethics
Technically
the branch of philosophy dealing with
values relating to human conduct, with
respect to the rightness and wrongness
of actions
Literally
ancient Greek: ethos, means
character