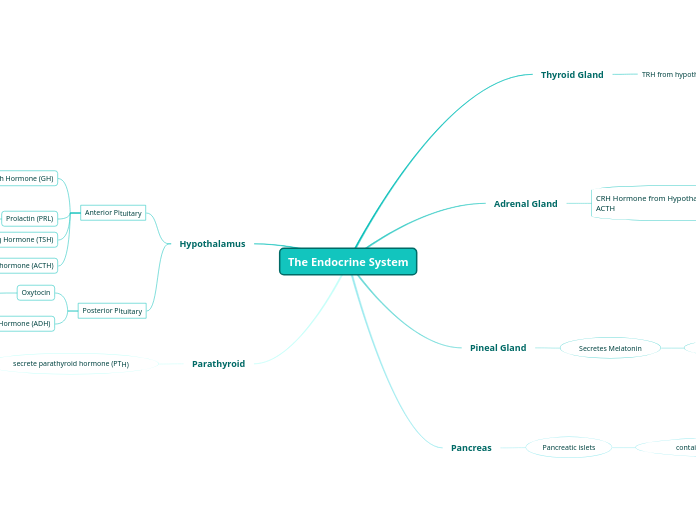
The Endocrine System
Parathyroid
secrete parathyroid hormone (PTH)
PTH stimulates the breakdown of bone and releases calcium into the blood.
Is responsible for maintaining the right amount of calcium in our blood.
The main targets are; kidneys, skeletal system, and the intestine.
Pancreas
Pancreatic islets
contains endocrine cells, producing two hormones
insulin is produced by the beta cells
Insulin lowers blood glucose levels and prevents sugar levels from being raised too high
Glucagon is produced by the alpha cells
Glucagon's role is to help raise blood glucose levels
glucagon breaks down glycogen and then is released into the blood
Pineal Gland
Secretes Melatonin
Melatonin is secreted by Pinealocytes
The amounts of melatonin that is secreted is affected by the amount of light exposed to a person For example: When a person is going to bed they turn off all the lights to help them sleep because more melatonin is secreted in the dark
Melatonin helps regulate a persons circadian rhythms
Adrenal Gland
CRH Hormone from Hypothalamus stimulate ACTH
adrenal medulla
epinephrine
norepinephrine
Subtopic
adrenal cortex
Zona reticularis gonad corticoids
sex hormone
zona fasciculata - glucocorticoids
Cortisol
help with stress resistance, influence metabolism in the cell and, enhance vasoconstriction by rising blood pressure to distribute nutrient to cells.
zona glumerulosa - mineralocorticoids -
Aldosterone
secretion of Aldosterone is affected by: Renin-angiotensin- Aldosterone (RAAS), plasma concentration of K+, ACTH, and Atrial natriuretic peptides (ANP
regulate and stimulate NA+ reabsorption and K+ elimination by kidney.
Thyroid Gland
TRH from hypothalamus stimulate TSH
TSH stimulate Thyroid Hormone
Has 2 forms. T4 (thyroxin) 4 iodine atom and T3 (triiodothyronine) 3 iodine atom. transports via bloodstream by protein called (TBGs) thyroxine binding globulins
it is the major metabolic hormone. has calorgenic effect in body. regulates tissue growth and critical for skeletal and nervous system, maintain BP
Hypothalamus
Posterior Pituitary
Anti-Diuretic Hormone (ADH)
triggered when blood concentration is high (dehydrated), kidney tubules reabsorb more water and uterine formation is prevented
Oxytocin
Released during childbirth, stimulates uterine contractions
Anterior Pituitary
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
stimulates adrenal cortex to release corticosteroids like cortisol
Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH)
stimulates metabolic rate, increases basal metabolic rate and heat production
Prolactin (PRL)
stimulates milk production in females
Growth Hormone (GH)
Direct:
Promotes increased glucose levels
Indirect:
stimulates bone and skeletal muscle cells to enlarge and divide