作者:Jared Braganza 5 年以前
207
Brain Basics/Info Processing
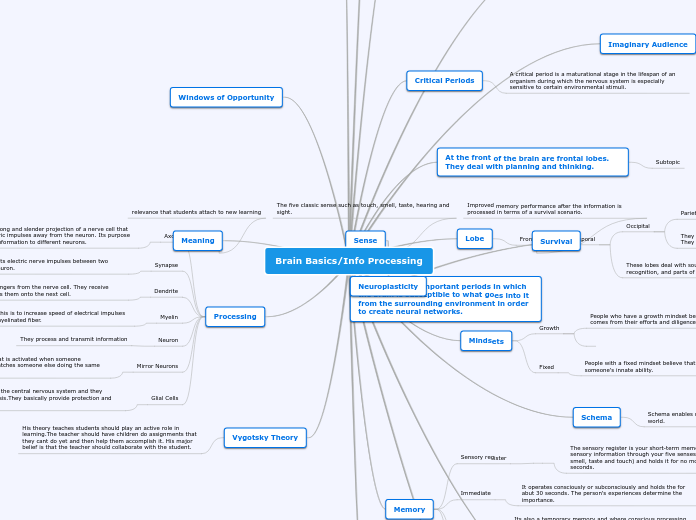
The brain's development and functionality are deeply influenced by its surrounding environment, shaping neural networks through critical periods of susceptibility. Different lobes of the brain, such as the frontal, temporal, occipital, and parietal, are responsible for integrating sensory information, visual processing, sound recognition, and long-term memory.