Floating topic
C1
C1.2
C1.2.1-Atomic structures
Subtopic
Elements
Substances whose atoms have the same atoms
have the same atomic number
Size of atoms
Atomic radii and bond length is typically around
10^-10 (0.1nm)
The length of the bond is the distance between
two joined atoms
The size of an atom is given by its
atomic radius(half its diameter)
C1.1
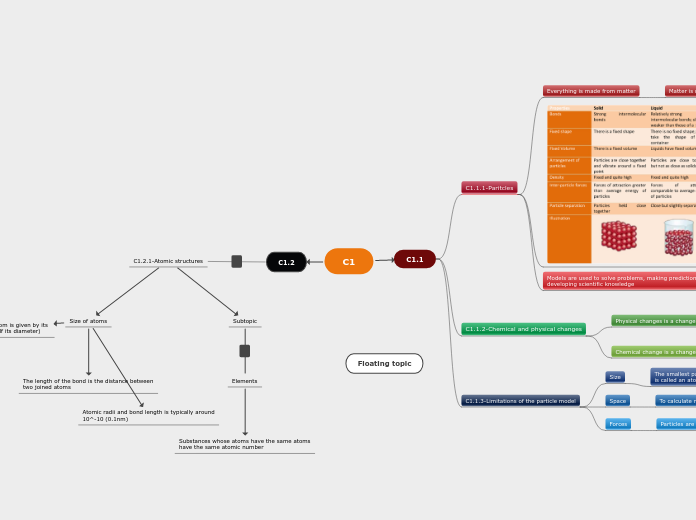
C1.1.3-Limitations of the particle model
Forces
Particles are held together by electrostatic forces
Forces of attraction between positive
and negative charges
The further the particles the weaker the forces
Space
To calculate ratio of an atom
Ratio= Distance between atoms
Diameter of atom
Size
The smallest particle that make up a substance
is called an atom
The smallest atoms are helium at 62x10^-12 m
in diameter
Distance between two helium is 55x larger than
diameter of the atom
C1.1.2-Chemical and physical changes
Chemical change is a change which produces new substances
It usually irreversible and creates a new substance
The particles then form in a different way
Physical changes is a change of state
Reversible and no new substances made
In a physical change the particles are the same
but their arrangement and movement change
E.g. Ice melting
C1.1.1-Paritcles
Models are used to solve problems, making predictions and developing scientific knowledge
The particle model is used to describe the arrangement of
particles and their different states
The particle model is used to explain certain properties
of a substance
Everything is made from matter
Matter is made from paritcles