作者:Illya Chang 4 年以前
253
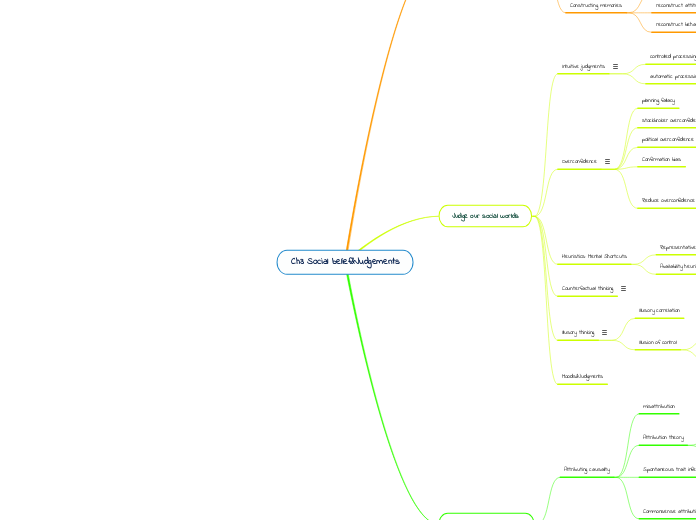
Ch3Socialbelief&Judgements
在社会心理学中,人们的信念和判断往往受到多种因素的影响,其中包括错觉思维、过度自信、直觉判断和归因理论。错觉思维如控制错觉和平均回归现象会影响人们对随机事件的解读;过度自信则可能源于能力不足或是计划谬误,政治和股票经纪人的过度自信也是常见现象。直觉判断是基于过去经验和家庭背景形成的,有时会通过启发式(如可得性启发和代表性启发)来简化决策过程,但也可能导致误判。
作者:Illya Chang 4 年以前
253

Self-awareness
Perspectives change with time
Camera perspective bias
Actor-observer perspectives
consensus
distinctivenss
consistency
situational attribution
dispositional attribution
<p>random events</p><p>错误地将neutral stimulus和UR连接在一起</p><p><br></p>
Regression toward the average
Gambling
<p>相似性(similarity)越高,越会产生counterfactual thinking(Ex:第一名和第二名)</p>
<p>增加知识=>降低直觉的危险性</p>
<p>能力不足的人会促进overconfidence(不自知)</p><p>Adler的(superiority)理论--人是自知的</p>
why their judgments might be wrong
unpack a task
prompt feedback
<p>受过去的experience\原生家庭的影响</p>
<p>信念很难改变</p><p>method to change it=>提醒他、鼓励他可以松动他的思维(不能强迫他)</p>