作者:Seto Seto 5 年以前
290
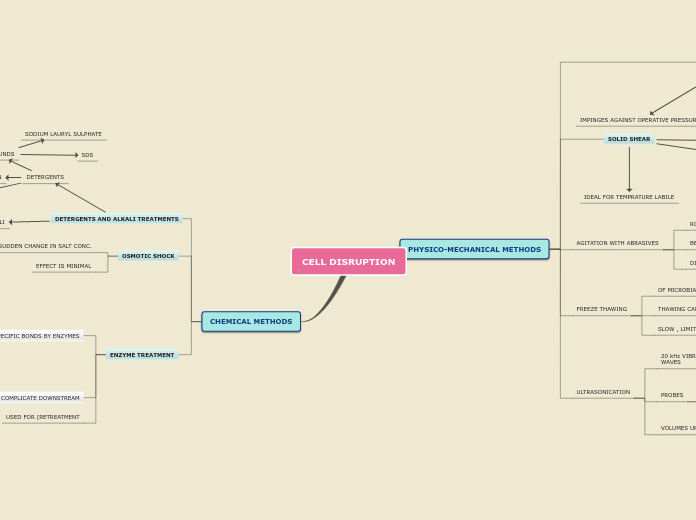
Classifying Metamorphic Rocks
Metamorphic rocks undergo substantial changes due to intense heat, pressure, or chemical fluids, often deep underground. The process of recrystallization involves minerals and grains being tightly packed together under these conditions, forming new crystal structures.