作者:Phung Ho 3 年以前
181
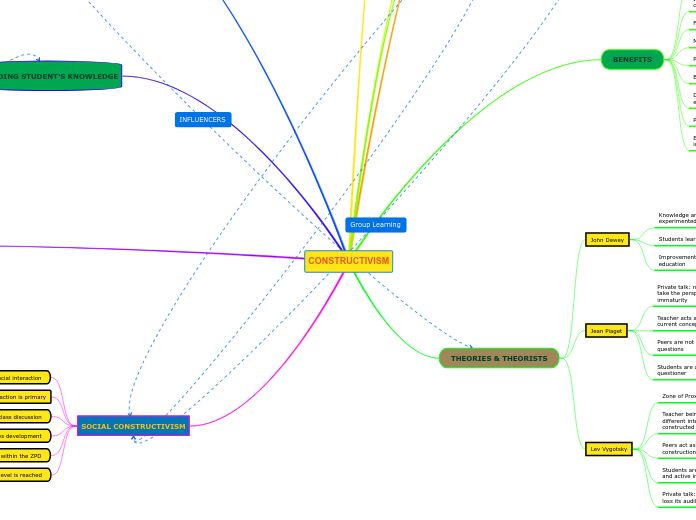
CONSTRUCTIVISM
The educational paradigm of constructivism emphasizes the learner's active role in the learning process, where cognitive and social interactions are key. This approach fosters collaboration, allowing students to pursue personal interests, engage in class discussions, and work together to solve problems.