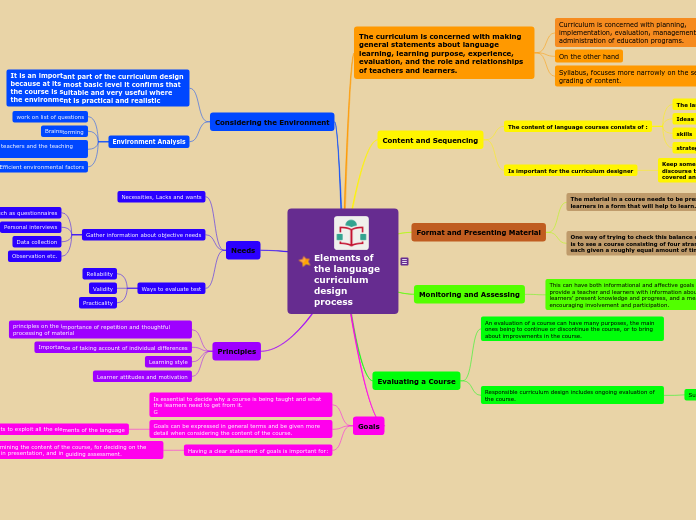
Elements of the language curriculum design process
jkmlñ
Goals
Having a clear statement of goals is important for:
Determining the content of the course, for deciding on the focus in presentation, and in guiding assessment.
Goals can be expressed in general terms and be given more detail when considering the content of the course.
Encourage students to exploit all the elements of the language
Is essential to decide why a course is being taught and what the learners need to get from it.
G
Principles
Learner attitudes and motivation
Learning style
Importance of taking account of individual differences
principles on the importance of repetition and thoughtful processing of material
Needs
Ways to evaluate test
Practicality
Validity
Reliability
Gather information about objective needs
Observation etc.
Data collection
Personal interviews
Such as questionnaires
Necessities, Lacks and wants
Considering the Environment
Environment Analysis
Efficient environmental factors
Focus on the nature of students, teachers and the teaching situation
Brainstorming
work on list of questions
It is an important part of the curriculum design because at its most basic level it confirms that the course is suitable and very useful where the environment is practical and realistic
Evaluating a Course
Responsible curriculum design includes ongoing evaluation of the course.
Summary of the Steps
7 Evaluate the course.
6 Include assessment procedures.
5 Design the lesson format.
4 Set goals, and choose and sequence content.
3 Decide on principles.
2 Assess needs.
1 Examine the environment.
An evaluation of a course can have many purposes, the main ones being to continue or discontinue the course, or to bring about improvements in the course.
Monitoring and Assessing
This can have both informational and affective goals that can provide a teacher and learners with information about the learners’ present knowledge and progress, and a means of encouraging involvement and participation.
Format and Presenting Material
One way of trying to check this balance of opportunities is to see a course consisting of four strands which are each given a roughly equal amount of time.
Fluency development.
Language-focused learning.
Meaning-focused output.
Meaning-focused input.
The material in a course needs to be presented to learners in a form that will help to learn.
Content and Sequencing
Is important for the curriculum designer
Keep some check on vocabulary, grammar, and discourse to make sure that important items are being covered and repeated.
The content of language courses consists of :
strategies that meet the goals of the course.
skills
Ideas
The language items
The curriculum is concerned with making
general statements about language learning, learning purpose, experience, evaluation, and the role and relationships of teachers and learners.
Syllabus, focuses more narrowly on the selection and grading of content.
On the other hand
Curriculum is concerned with planning, implementation, evaluation, management, and administration of education programs.