Uremia
- Buildup of toxins in blood
- Kidneys stop filtering toxins out through your urine
High urea accumulation
- Medication
- Dialysis & kidney transplant surgery
Excess urea is removed by hemodialysis
Blood is drained from whichever artery is convenient and is sent to the dialyzing unit
Nephritis
- Medication
- Special treatment (removes excess fluid & dangerous protein)
- Certain chemicals
- Genetics
- Infection or inflammatory conditions (lupus)
- Inflamed nephrons (glomerulonephritis)
- Affects kidney function
- Pain in pelvis
- Burning sensation in urine
- Cloudy or bloody urine
- Pain in kidney
- Vomiting
- Produced in the brain
- Regulate the amount of water excreted by the kidneys
Juxtaglomerular cells
Antidiuretic hormone
Substances filtered into bowman's capsule from glomerulus
- Na+, Cl- & H+
- Nitrogenous wastes (amino acids, urea, uric acid)
- Vitamins/minerals
- ions reabsorbed
- H+ ions secreted
- Water leaves through aquaporins
- Water exits through aquaporins (descending)
- Na+ & Cl- actively transported out (ascending)
Cortex into medulla
Floating topic
- K+ & Na+ secreted via active transport into urine
- Na+ & Cl- reabsorbed
- Water moves into urine through aquaporins
Cortex
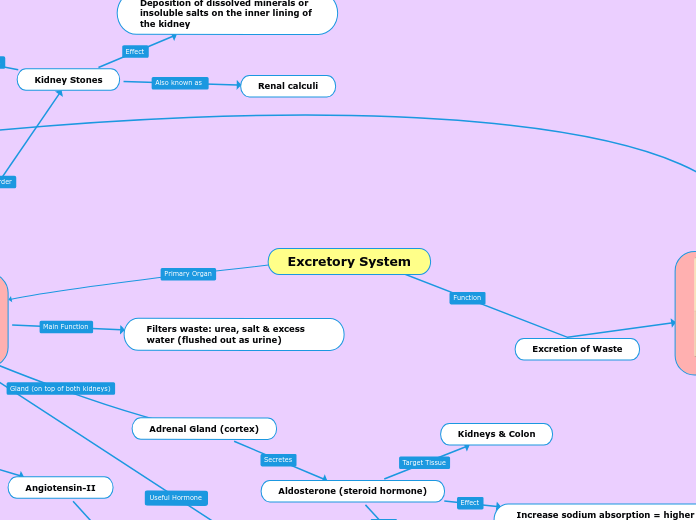
Excretion of Waste
- Water moves out via aquaporins
- Urea exits (no movement of ions)
cortex through medulla, into renal pelvis
Funnels urine via peristalsis into the ureter
Excretory System
Urine Formation
Secretion
Reabsorption
Filtration
Kidney
Kidney Stones
- Severe pain
- Nausea
- Fever/chills and
- Blood in your urine
Renal calculi
Deposition of dissolved minerals or insoluble salts on the inner lining of the kidney
Renin
- Controls blood pressure
- Maintains healthy levels of sodium & potassium
- Released in bloodstream when blood pressure is low
Angiotensin-II
Blood vessels, smooth muscles & adrenal cortex
Adrenal Gland (cortex)
Aldosterone (steroid hormone)
Kidneys & Colon
Signals colon and kidneys to put more sodium in bloodstream or release more potassium into urine
Increase sodium absorption = higher blood pressure
Filters waste: urea, salt & excess water (flushed out as urine)
Nephrons
Renal Pelvis
Collecting Ducts
Distal Convoluted Tubule
Loop of Henle
Proximal Convoluted Tubule
Bowman's Capsule
Glomerulus