作者:Farah Aina Anas 9 年以前
442
LANGUAGE LEARNING STRATEGIES
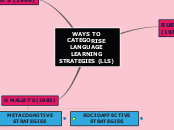
Language learning strategies can be categorized into various frameworks by different scholars. Oxford's model from 1990 divides these strategies into direct and indirect categories:
作者:Farah Aina Anas 9 年以前
442

更多类似内容
Related with social-mediating activity and transacting with others. Cooperation and question for clarification are the main socioaffective strategies.
Strategies which require planning for learning, thinking about the learning process, monitoring of ones production or comprehension and evaluating learning after an activity is completed
More limited to specific learning task & it involves more direct manipulation of the learning materials itself
A. Asking questions
B. Cooperating with others
C. Emphatising with others
A. Lowering your anxiety
B. Encouraging yourself
C. Taking your emotional temperature
A. Centering your learning
B. Arranging & planning your learning
C. Evaluating your learning
A. Creating mental linkages
B. Applying images & sounds
C. Reviewing well
D. Employing action
A. Practising
B. Receiving & sending messages strategies
C. Analysing & reasoning
D. Creating Structure
* input
* output
A. Guessing intelligently
B. Overcoming Limitations
*speaking
*writing
Activities learners engage in which afford them opportunities to be exposed to practise their knowledge
Less directly related to language learning since their focus is on the process of participating in a conversation
Used to oversee, regulate & self-direct language learning
Steps or operations used or problem-solving