life Science
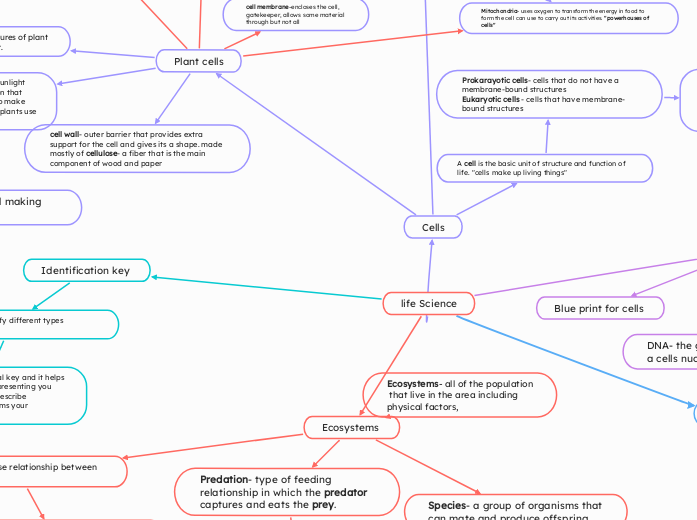
Identification key
can be used to identify different types organism
A Dichotomous key is a special key and it helps you identify an organism by presenting you with a series of choices that describe characteristics of the organisms your identifying
Classification Hierarchy
The groups that have the largest number of different organisms are called domains. There are three domains archaea, bacteria and eukarya
The next level in the hierarchy is called kingdom. The domain archaea and bacteria only have one kingdom while eukarya has four plants, animals, fungi and protists
Cells
Plant cells
Chlorophyll- captures the nergery of sunlight and uses it to from a chemical reaction that combines water and carbon dioxide to make glucose- which makes a simple sugar plants use as food.
Photosynthesis the food making process.
chloroplasts- food making structures of plant cells, contains the green pigment.
cell wall- outer barrier that provides extra support for the cell and gives its a shape. made mostly of cellulose- a fiber that is the main component of wood and paper
Animal cell
Mitochondria- uses oxygen to transform the energy in food to form the cell can use to carry out its activities. "powerhouses of cells"
Vacuoles- fluid filled structures temporarily store different substances needed. some are specialized to store waste product. Animal cells often have many vacuoles.
Cytoplasm- gel like fluid takes up
most of the space in a cell.Mostly
water with other substances dissolved.
throughout the cytoplasm are many
structures called organelles- carry out
the activities that keep the cells alive
Nucleus- located near the center of a animal cell
the nucleus is home to the cells chromosomes - Genetic structures that contain the information used to direct cell activity and make new cells.
Nucleolus- found inside the nucleus. Is responsible for making ribosomes which are then transported to the cytoplasm.
Nuclear membrane- surrounds and protects the nucleus
cell membrane-encloses the cell,
gatekeeper, allows some material
through but not all
A cell is the basic unit of structure and function of life. "cells make up living things"
Prokarayotic cells- cells that do not have a membrane-bound structures Eukaryotic cells - cells that have membrane-bound structures
Unicellular- made of only one cell the single cell carries out all of the activities that keep the organism alow it to reproduce ex. Escherichia coli,Diatoms, Protozoa Protista, Streptococcus. Multicellular- made of many cells these cells work together to keep the organism alive and reproducing ex. earthworms, trees, mushrooms and humans
in Multicellular organisms many cells are specialized to do one job this allows them to be able to perform so many functions
Dna
Genes- segments of DNA that carry instructions for the traits of a organism from parent to offspring.
your genes determine your traits
Blue print for cells
DNA- the genetic material found is a cells nucleus
Ecosystems
Symbiosis- a close relationship between two species.
Parasitism- occurs when a parasitic
organism feeds on the cells , tissue and fluids of another organism.
Commensalism- a relationship where one species benefit and the other is unaffected.
Mutualism - a relationship in which both species benefiet
Predation- type of feeding relationship in which the predator captures and eats the prey.
prevents overpopulation from happening in the ecosystem
Ecosystems- all of the population
that live in the area including
physical factors,
Species- a group of organisms that can mate and produce offspring
Populations- where organisms of the same species live in the same place at the same time. ex mice living in a small meadow. all pines trees in a Forrest.
limiting factors-
water
living space
light
food
Community- populations share the environment to create a..