作者:MARTIN ALAVEZ RAMIREZ 5 年以前
389
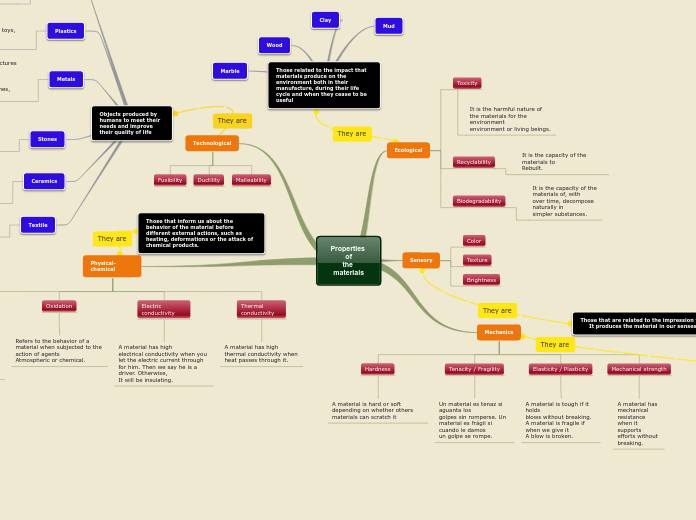
Properties of the materials
Materials used in various industries can be classified based on their physical and chemical properties, as well as their sensory impact and ecological footprint. These materials are essential in construction, manufacturing, and daily life.