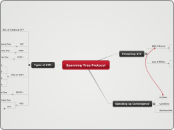
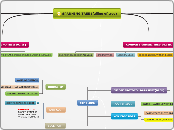
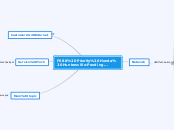
Spanning Tree Protocol
Types of STP:
MST
IST
Internal Spanning Tree
Multiple Spanning Tree
RPVST+
Rapid Per-VLAN Spanning Tree
802.1w RSTP
Port Types
point-to-point port
If on a shared media(half duplex)
Because multiple switches might be involved.
Must go through traditional 802.1D convergence
Root port
Edge port
No longer edge if BPDU received
Host Port
Differences
BPDUs sent from all switches
Discarding
Backup Port
Alternate Port
PVST+
Per-VLAN Spanning Tree Plus
Operates over both dot1Q and ISL
Interoperability betwen CST/PVST
PVST
Per-VLAN Spanning Tree
ISL Based
1 instance of STP per VLAN
CST
Common Spanning Tree
dot1Q based
Over the Native VLAN
1 instace of STP
802.1D Traditional STP
Timers
MaxAge (20 Seconds)
Forward Delay(15 Seconds)
Hello Time (2 Seconds)
Port States
Forwarding
Learning
Listening
Blocking
Disabled
Port Roles
Blocking Port
Designated Port
Root Port
Speeding up Convergence
BackboneFast
UplinkFast
Portfast
Protecting STP
Loss of BPDUs
UDLD
Works by sending keepalives
Unidirecitonal Link Detection
Loop Guard
Doesn't actually detect unidirecitonal links
With Loop Guard: Port Becomes Loop-inconsistent
W/O Loop Guard: Port Starts Forwarding
Simply detects loss of BPDUs
BPDU Filtering
Requires PortFast
Disables BPDUs on a port(Dangerous)