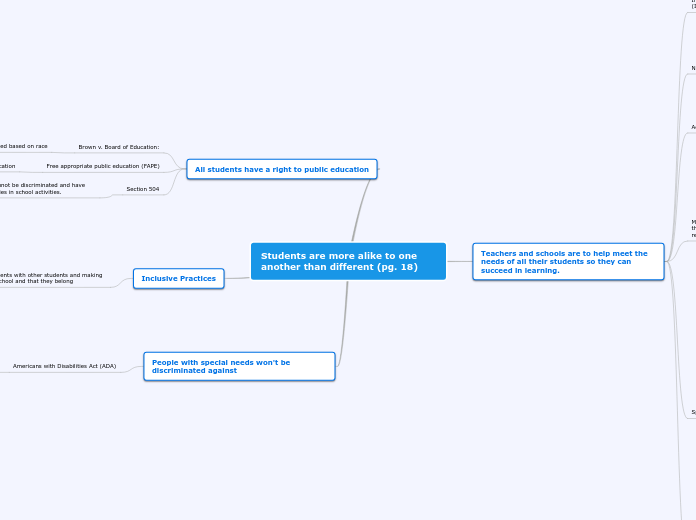
Students are more alike to one another than different (pg. 18)
People with special needs won't be discriminated against
Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA)
A law that mandates that no one with disabilities will be discriminated by employers or businesses. Businesses, establishments, and employers must make accommodations and modifications to meet their needs and help them succeed.
Inclusive Practices
Integrating disabled students with other students and making them feel welcomed at school and that they belong
Making sure that disabled students are taught the same curriculum as the rest of the school.
Nurturing relationships between students with disabilities and with no disabilities in order to create a support system
All students have a right to public education
Section 504
Students with disabilities cannot be discriminated and have the right to equal opportunities in school activities.
Free appropriate public education (FAPE)
Disabled students have a right to public education
Brown v. Board of Education:
Students can't be discriminated based on race
Teachers and schools are to help meet the needs of all their students so they can succeed in learning.
Evidence-based practice: The ESEA and IDEA both demand that teachers and professionals use strategies and instruction that is proven to work and be effective in teaching children.
Special education:
Education designed to meet the needs of those with disabilities and help them learn and progress.
Low-incidence disabilities: Less common disabilities that involve hearing impairments and autism.
High-incidence disabilities: The most common disabilities, such as speech impairment and ADHD.
Student need to be appropriately evaluated to see if they need to be part of the special education program.
Multi-tiered system of support (MTSS): A system created to meet struggling students’ needs. Professionals use this system to better communicate with each other, the parents, and teachers in order to find resources to best help the students and identify solutions.
Nondiscriminatory evaluation: A law that says students must be assessed without any discrimination toward their race or disability.
Positive behavior supports (PBS): Where schools work to identify the reason behind problematic behavior in students and find solutions before things get out of hand and the situation worsens.
Response to intervention (RtI): Instead of just using tests to determine if students need special education, this requires that professionals place them under instructional interventions to see whether they improve or not. If they don’t, then they need special education.
Modifications: improving the effectiveness of a lesson to meet the needs of a student by changing what is taught or removing some of it.
Individualized education program (IEP): The curriculum program and plan written out by professionals and parents that guidelines how the student will be taught and what accommodations and modifications to the curriculum are needed.
Cross-categorical approach: This helps teachers be more effective in helping their disabled students by not just using strategies from one category of disability, but by trying to incorporate strategies from multiple categories.
Specially designed instruction: instruction that is modified to meet the needs of disabled students. It involves monitoring their progress and improving various skills such as in communication, academics, and behavior.
Accommodations
Related services: Added assistance outside of academics to better help disabled students thrive. This could be from physical therapy, to speech therapy, and so on.
Supplementary aids and services: Accommodations given to disabled students to help them thrive in their learning in classrooms with students who don’t have disabilities.
No Child Left Behind Act of 2001
This act mandates standards that are meant to improve students’ academic success, including students with disabilities. It’s improved the course content of the core subjects and has made it mandatory that they are taught by qualified teachers to all students.
Individuals with Disabilities Education Improvement Act (IDEA)
Elementary and Secondary Education Act of 1965 (ESEA): a law passed that sets standards to the education of all students.
Least restrictive environment (LRE): it’s a law that says disabled students should have the same classroom environment as the students without disabilities, and that separate classrooms should only be used to extend their learning.