The
Junior
Learner
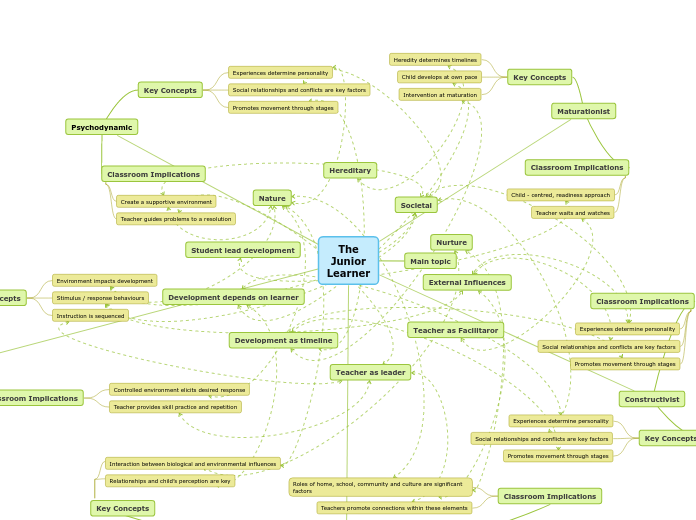
The document discusses various educational theories and their implications in the classroom. The maturationist perspective emphasizes that child development follows a predetermined timeline largely influenced by heredity, with teachers adopting a child-centered, readiness approach.
開啟
Nurture Nature Student lead development Hereditary Teacher as Facilitaror Teacher as leader External Influences Development as timeline Development depends on learner Societal Maturationist Teacher waits and watches Child - centred, readiness approach Intervention at maturation Child develops at own pace Heredity determines timelines Constructivist Interactionist Ecological Teachers promote connections within these elements Roles of home, school, community and culture are significant factors Relationships and child’s perception are key Interaction between biological and environmental influences Psychodynamic Teacher guides problems to a resolution Create a supportive environment Promotes movement through stages Social relationships and conflicts are key factors Experiences determine personality Behavioural Classroom Implications Teacher provides skill practice and repetition Controlled environment elicits desired response Key Concepts Instruction is sequenced Stimulus / response behaviours Environment impacts development The
Junior
Learner Main topic