by Adam Miceli 4 years ago
261
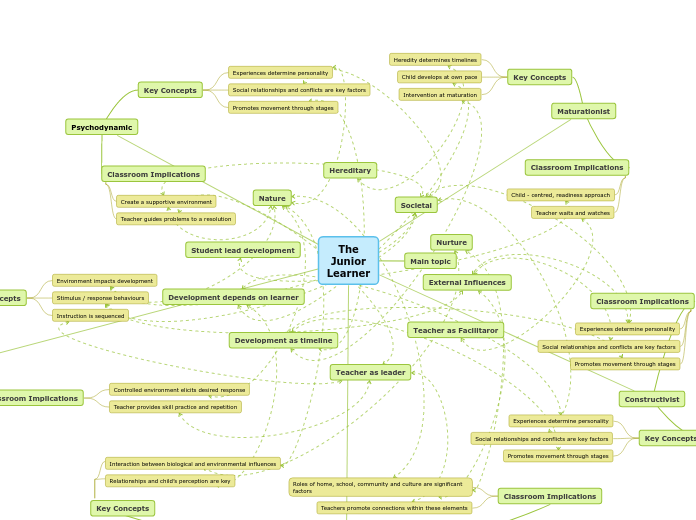
The Junior Learner
The document discusses various educational theories and their implications in the classroom. The maturationist perspective emphasizes that child development follows a predetermined timeline largely influenced by heredity, with teachers adopting a child-centered, readiness approach.