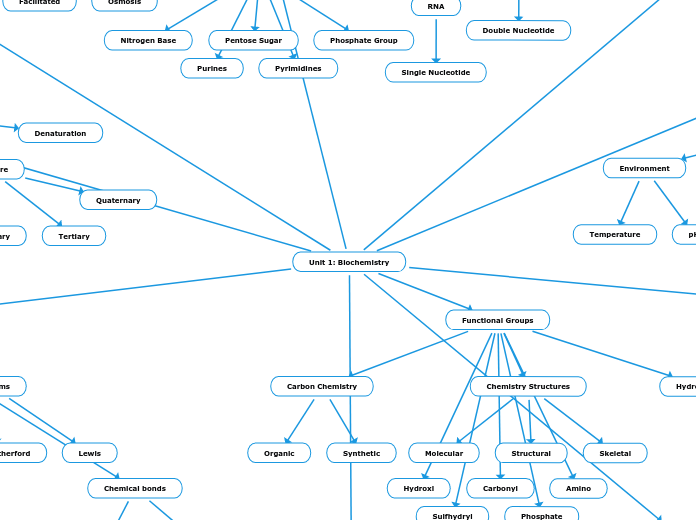
Unit 1: Biochemistry
Cell Transport
Exocytosis
Endocytosis
Hypertonic
Hypotonic
Isotonic
Active
Bulk
Passive
Osmosis
Facilitated
Concentration Gradient
Homeostasis
Fluid Mosaic Model
Integral
Peripheral
Fluidity
Cholesterol
Fatty Acid Tail Length
Double Bonds
Cell Membrane
Neutral Lipid
Glycolipid
Phospholipid
Nucleic Acid
Hydrogen Bonds
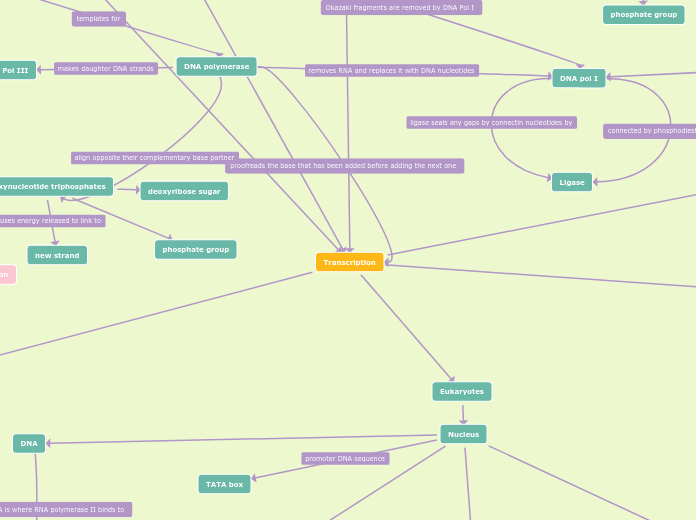
Nucleotides
Pyrimidines
Purines
Phosphate Group
Pentose Sugar
Nitrogen Base
DNA
Double Nucleotide
RNA
Single Nucleotide
Enzymes
Factors that Affect Activity
Regulation
Allosteric
Non-Competitive Inhibitor
Competitive Inhibitor
Cofactors/Coenzymes
Environment
pH
Temperature
Induced Fit
Lock and Key
Catalyst
Activation Energy
Proteins
Renaturation
Denaturation
Structure
Quaternary
Tertiary
Secondary
Primary
Peptide Bond
Polypeptide
Amino Acids
Electrically Charged
Lipids
Fatty Acids
Types
Waxes
Sterols/Steroids
Phospholipids
Triglycerides
Orientation of Hydrogen Around Double Bonds
Hydrogenation
Location of Double Bonds
Degree of Saturation
Saturation
Length of Carbon Chain
Carbohydrates
Complex
Glyosidic Bonds
Branches
Coiled
Polysaccharides
Chitin
Cellulose
Dietary Fiber
Glycogen
Starch
Ketone
Aldehyde
Simple
Disaccharides
Monosaccharides
Biochemical Reactions
Chemical Reactions
Oxidation
Neutralization
Hydrolysis
Condensation
Macromolecules
Polymer
Monomers
Functional Groups
Phosphate
Sulfhydryl
Amino
Carbonyl
Hydroxl
Hydrocarbons
Chemistry Structures
Skeletal
Structural
Molecular
Carbon Chemistry
Synthetic
Chemistry Fundamentals
Electronegativity
Chemical bonds
Ionic
Intramolecular Bonds
Non-Polar
Polar
Isotopes
Harmful/Helpful
Half Life
Radioisotopes
Nuclear Medicine
Radioactive Tracers
Atomic Number
Diagrams
Lewis
Bohr-Rutherford
Standard
Compounds
Inorganic
Organic
Elements