Musculoskeletal System
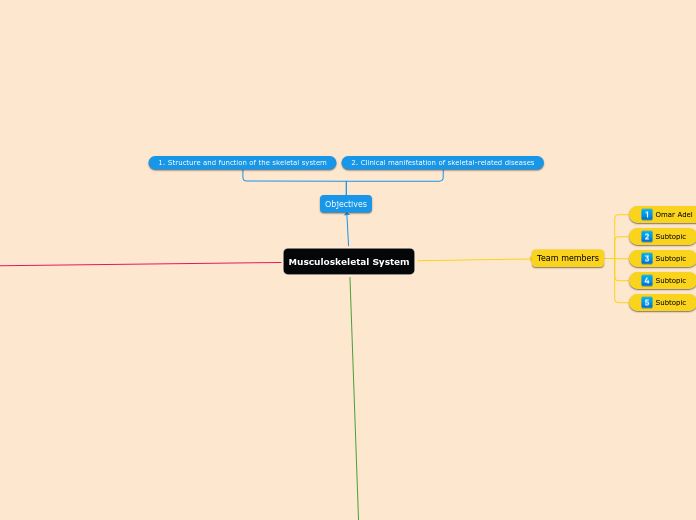
Team members
Subtopic
Omar Adel
Clinical manifestation of skeletal-related diseases
Muscular dystrophy
severe form
Osteoporosis
stooped posture
Bone fracture
Arthritis
3 common types
Gout
Osteoarthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis
one of the most common skeletal-related disease
Rickets
manifestations
Delayed growth
caused by
Objectives
2. Clinical manifestation of skeletal-related diseases
1. Structure and function of the skeletal system
Structure and function of the skeletal system
How our bones are repaired?
Bone growth
How do bone forms?
Endochondral bone formation
Intramembranous bone formation
Strength and thickness of the bones
What are the cells that can be found in bones?
osteoclasts
They remove the bone matrix
by phagocytosis, dissolve the bone salts, and release the calcium and phosphate ions
into the circulation
multinucleated cells related to
macrophages, are concerned with bone resorption.
osteocytes
Make the bone calefied and more rigid, osteoblasts
become incorporated within the bone and become transformed into relatively inactive mature bone cells called osteocytes.
Mature Osteoblast
osteoblasts
relation with mitosis
Dont undergo mitosis
function/purpose
secrete an enzyme, alkaline phosphatase, that promotes deposition of calcium phosphate salts in the bone matrix to calcify the bone
definition
active bone-forming
cells that produce the collagenous bone matrix.
What is skeleton?
XXXXXXX
What are the types of bone?
bones vary in size and appearance
irregular
protect various parts of your body. Eg, your vertebrae protect your spinal cord.
vary in shape and structure and therefore do not fit into any other category. have a fairly complex shape, which helps protect internal organs
vertebrae, sacrum, coccyx, temporal, sphenoid, ethmoid, zygomatic, maxilla, mandible, palatine, inferior nasal concha, and hyoid.
flat
protect internal organs such as the brain, heart, and pelvic organs.
two thin layers of compact bone enclosing between them a variable quantity of cancellous bone, which is the location of red bone marrow.
occipital, parietal, frontal, nasal, lacrimal, vomer, hip bone (coxal bone), sternum, ribs, and scapulae
short
provide stability to the wrist and ankle joints and also help facilitate some movements.
shaped roughly as a cube and contain mostly spongy bone. The outside surface is comprised of a thin layer of compact bone.
include the carpal bones of the hands that allow movement of the wrist, and the tarsal bones of the feet that allow movement of the ankle.
long
purpose
provides considerable strength without excessive weight.
The parts of a typical long bone are referred to by specific terms.
the shape
e long cylindrical part,
and the expanded ends of the shaft are called the epiphyses. The center of the shaft is
hollowed out to form the marrow cavity, which is filled with fat and bone marrow.
where is it usually found?
upper and lower
limbs, has a tubular shape with expanded ends.
cancellous bone
contains a high number of bone cells and is responsible for changes in bone growth and structure.
Inner, spongy layer of bone
cortical bone
mechanical strength and makes up the majority of the skeleton.
Outer layer of compact layer