Made of
Nucleotides
Nitrogen Base
5 Carbon Sugar
Phosphate
managed by
energy coupling
coupled
Ligase
DNA Pol 1
Ester
traveling through
Proteins synthesized here are made in cytosol and go to these locations.
Primase
Dehydration Synthesis
Helicase
Lagging Strand
ALWAYS 5' - 3'
To enter the E.R.
SSB
binds to
which binds to the
SRP is removed, and
Protein released in ER
Leading Strand
Branched
DNA Pol III
yielding
bonds break by
Long Hydrocarbon Chains
drives an
Kinks
Made Of
REDUCTION
Oxidation
Electron Carrier
Big Idea I: Structure Relates Function
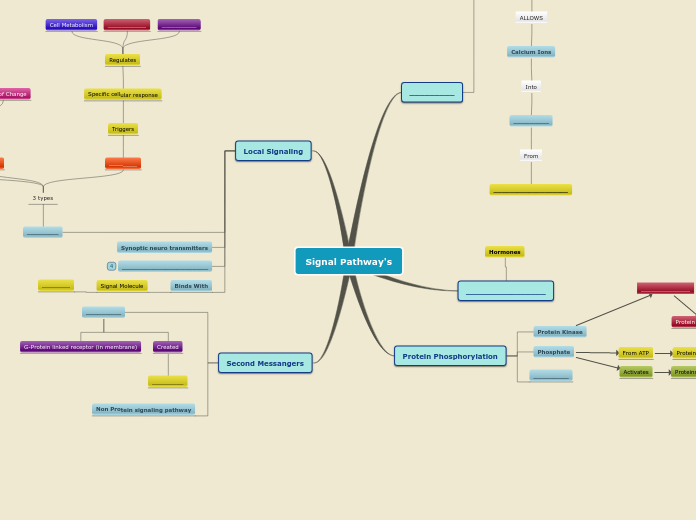
5D. Polypeptide Synthesis
Bound Ribosomes
Endomembrane System
for secretion
Vacuoles
Lysosomes
Golgi Apparatus
modify the protein
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Signal Regocgnition particle
Signal Peptide (End of synthesized peptide -during transcription)
Receptor Protein
Synthesis Continues in ER Lumen Membrane
Signal Peptide Removed
protein can now enter
Vesicles
aid in cell motility
powered by motor proteins
which attach to microtubules or filaments
part of cytoskeleton
Free Ribosomes
Etc, outside of endomembrane system
Choloroplast
Peroxisomes
Mitochondria
Cytosol
(3A) Biological Molecules
Lipids
forms bilayer in aqueous solution
Steroids
5 Rings - Cholesterol
Plasma Membrane
Vitamin D
Sex Hormones
Phospholipids
Hydrophobic Tails
Hydrophilic Heads
Tryglyceride
3 Fatty Acids
Unsaturated
Trans
H bond below
Cis
H bond above
Saturated
Glycerol
Nucleic Acids
RNA
Uracil - no thymine
Types
tRNA
mRNA
rRNA
DNA
Pyrimidines
Thymine
Cytosine
Purines
Guanine
Proteins
Primary
Sequence of Amino Acids
Secondary
Tertiary
Hydrogen
Ionic
Hydrophobic
Quaternary
Final Coiled Protein
Disulfide Bridges - Folding
Beta Pleated Sheets
Alpha Helix
Polypeptide Chains
Amino Acids
Acidic
-
Basic
+
NonPolar
CH3
Polar
OH, SH, NH
Carbohydrates
Complex Sugars
Polysaccharides
Cellulose
Beta Glucose
Structure/Plant
Glycogen
Energy/Animal
Starch
Alpha Glucose
Amylopectin
Amylose
Energy/Plant
5 Carbon
C6H12O6
Big Idea II: Energy is Stored Used and Transformed
9A. Cellular Respiration
ETC
H2O
Chemiosmosis
Kreb's Cycle
FADH2
Oxidation of Pyruvate
2 AcetylCoa
Glycolysis
Glucose
NADH
ATP
Substrate-Level Phosphorylation
2 Pyruvate
8C. ATP (Adenosine triphosphate)
Uses
Mechanical work
binding to motor proteins - ATP hydrolyzed
Transport work
phosphorylation of protein
Chemical Work
Exergonic Process
Endergonic Process
synthesis of amino acid
*need a phosphorylated intermediate
Structure
3 Phosphate Groups
Hydrolysis
- phosphate
yields ENERGY
+ H2O
Adenine
Ribose
Big Idea III: Genetic Information is Transmitted Through Generations and Expressed in a Regulated Manner
12F. Transcription/Translation
contains terminator sequence
contains Ribosome Binding Site
during transcription
Cytoplasm
Translation
When?
after transcription
Transcription
transcription factors
Produces
Pre-mRNA
poly A tail
5' CAP
RNA Processing
Spliceosomes
mature mRNA
Where?
Nucleus
11D. Replication
Prokaryotes
have only one ORI sequence
Eukaryotes
Have 100s of ORI Sequences
Strands Separated at ORI Sequence
Strands run Anti-Parallel
Strands Do Not Latch Back Together
RNA Primer placed down
DNA Nucleotides laid down
RNA Primers Removed
links Okazaki fragments
Strand continues