von Eunice Resurreccion Vor 2 Jahren
214
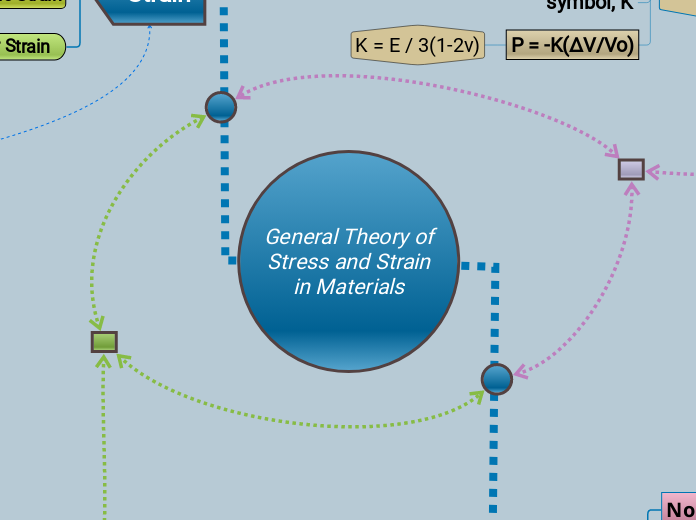
General Theory of Stress and Strain in Materials
The study of stress and strain in materials explores how different forces affect the deformation and behavior of materials. The stress-strain curve is crucial for understanding these properties, showing the relationship between the applied stress and the resulting strain.