von Sebastian Birch Schmidt Vor 12 Monaten
103
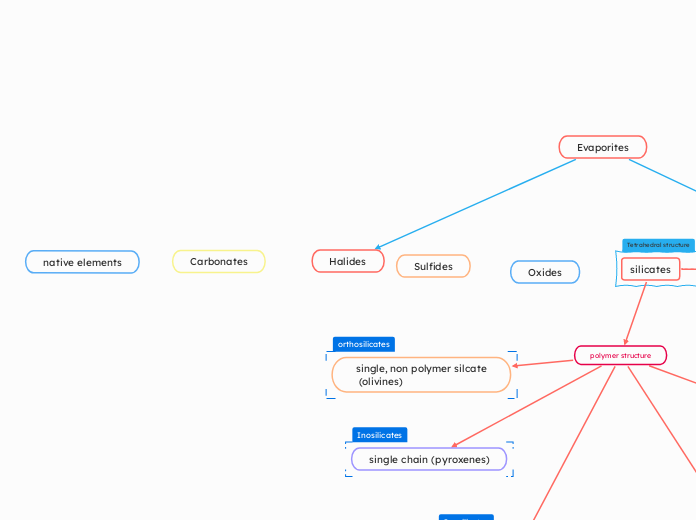
Halides
The discussion revolves around the properties and behaviors of various minerals and their interactions with cations, particularly focusing on the differences in ion sizes such as Al+3 and Fe+.
von Sebastian Birch Schmidt Vor 12 Monaten
103

Mehr dazu