von Michelle Hahn Vor 4 Jahren
767
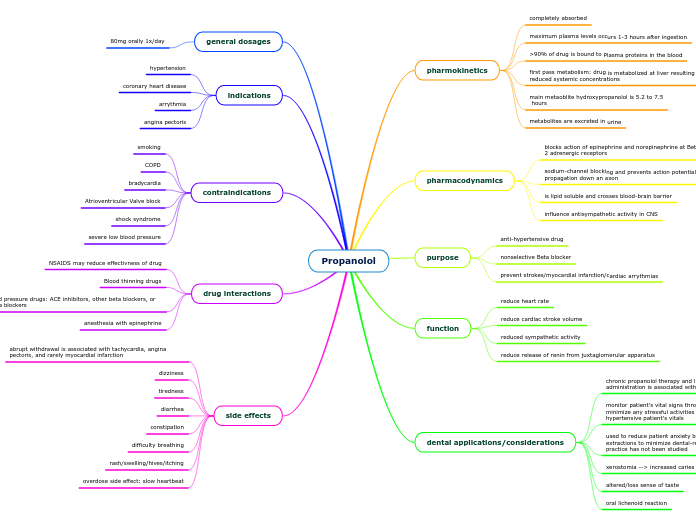
Propanolol concept map
Propanolol, a nonselective beta blocker, is extensively used to treat various cardiovascular conditions such as hypertension, angina, coronary heart disease, and arrhythmias. It is completely absorbed in the body, with maximum plasma concentrations occurring within 1 to 3 hours post-ingestion.