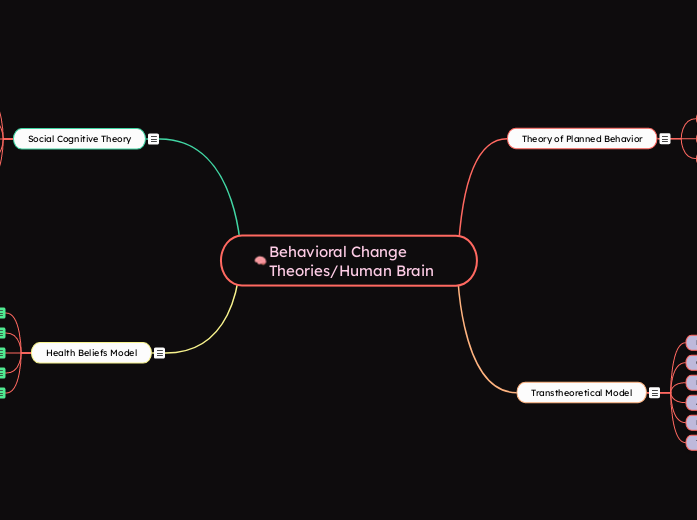
Behavioral Change Theories/Human Brain
Health Beliefs Model
A psychological framework that helps explain and predict health behaviors. The model focuses on how people perceive health threats and decide whether to take action.
Cues to Action
Internal or External stimuli that trigger the decision-making process.
Perceived Barriers
Belief that they are barriers to taking action.
Perceived Benefits
Belief that taking action will have positive benefits.
Perceived Severity
The feelings concerning the seriousness of contracting an illness.
Perceived Susceptibility
Belief that a person is likely to contract a health condition.
Social Cognitive Theory
A theory that explains how people learn and behave by considering the interaction between their personal factors, their environment, and their behavior. SCT is based on the idea that people learn through their own experiences, but also by observing others and the results of their actions.
Behavioral Capability
The understanding and having the skill to perform a behavior.
Observational learning
Paying attention to reinforcement, self control, and self-efficacy and how these elements are influencing behavior.
Reciprocal Determinism
Dynamic interaction between people, their behavior, and their environment.
Self-Efficacy Expectation
The belief and expectation that an individual has control over and is able to execute a behavior.
Outcome Expectation
Expectations about the outcome that will result from engaging in behavior.
Transtheoretical Model
A theory that helps people change their behaviors by identifying stages of change and providing strategies to guide the process.
Termination
The person no longer wants to return to their previous negative behaviors.
Maintenance
The person continues to make changes to sustain the behavior.
Action
The person makes significant behavioral changes to alter their previous pattern.
Preparation
The person starts to make some behavioral changes.
Contemplation
The person acknowledges a problem and considers changing in the future.
Precontemplation
The person doesn't acknowledge a problem and doesn't consider changing.
Theory of Planned Behavior
TPB is a social psychology theory that explains how people decide to behave based on intentions.
Subjective norms
The social norms, cultural beliefs, and groups opinions that surround an individual.
Perceived Behavioral Control
An individuals perception of how much control they have over behavior.
Attitude
An individual's belief about whether a behavior is good or bad for them.