por Ashley Oxendine hace 2 años
315
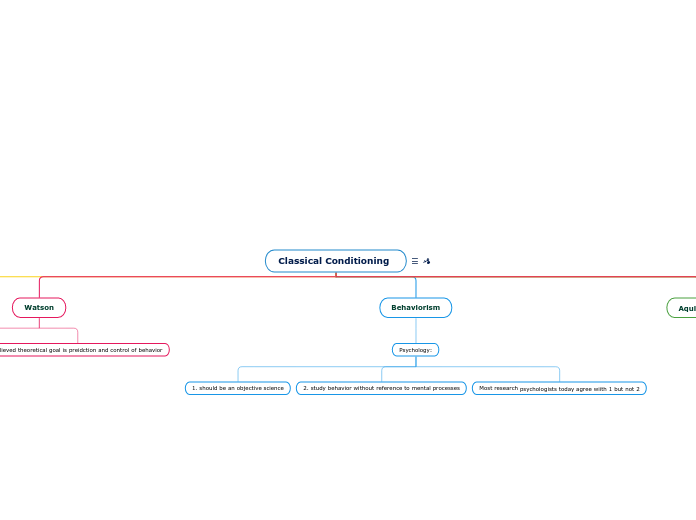
Classical Conditioning
Classical conditioning is a foundational process of learning applicable across species, as demonstrated by Pavlov's experiments with associative learning. His work laid the groundwork for understanding how organisms respond to stimuli, influencing areas such as health, motivation, emotion, and psychological therapy.