por Gaby Ramirez hace 4 años
305
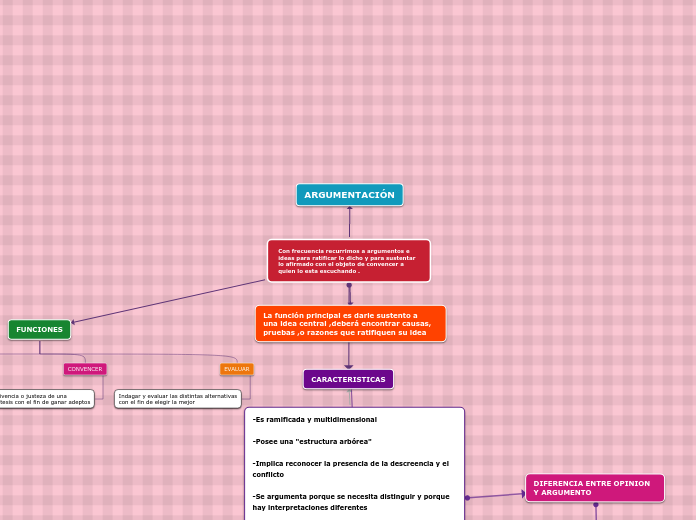
Con frecuencia recurrimos a argumentos e ideas para ratificar lo dicho y para sustentar lo afirmado con el objeto de convencer a quien lo esta escuchando .
La argumentación es una habilidad crucial en el ámbito educativo, ya que permite desarrollar el pensamiento crítico en los jóvenes. Las competencias argumentativas en la escuela abarcan la capacidad de elaborar exposiciones, escribir ensayos y analizar películas, entre otras actividades.