Disease Prevention
Heba Azeef - TPJ4M
Instrument processing
Decontamination
soaking instruments in disinfectant
Cleaning
scrub equipment to remove organic matter
high-level disinfection
used when sterilization is not possible
boiling
Sterilization
kill all microorganisms
pressure steam
dry heat
chemical
use or storage
Definitions: asepsis, disinfection, sterilization
Sterilizer - destroys all microorganisms.
Sterilized - absence of all microrganisms
Ex, autoclave
Disinfectant - chemicals that kill or prevent growth of pathogens on inanimate objects
Ex, bleach, zephirin
Antiseptic - chemicals that kill or prevent the growth of pathogens on living skin
Asepsis - absence of microrganisms on living skin and mucous membranes
Ex, alcohol, betadine
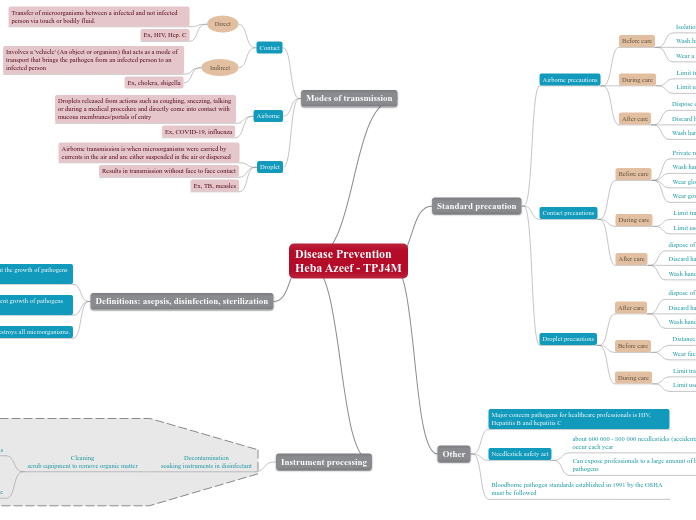
Modes of transmission
Droplet
Ex, TB, measles
Results in transmission without face to face contact
Airborne transmission is when microorganisms were carried by currents in the air and are either suspended in the air or dispersed
Airborne
Ex, COVID-19, influenza
Droplets released from actions such as coughing, sneezing, talking or during a medical procedure and directly come into contact with mucous membranes/portals of entry
Contact
Indirect
Ex, cholera, shigella
Involves a 'vehicle' (An object or organism) that acts as a mode of transport that brings the pathogen from an infected person to an infected person
Direct
Ex, HIV, Hep. C
Transfer of microorganisms between a infected and not infected person via touch or bodily fluid.
Other
Bloodborne pathogen standards established in 1991 by the OSHA must be followed
Needlestick safety act
Can expose professionals to a large amount of bloodborne pathogens
about 600 000 - 800 000 needlesticks (accidental needle pricks) occur each year
Major concern pathogens for healthcare professionals is HIV, Hepatitis B and hepatitis C
Standard precaution
Droplet precautions
Wear facial protection such as a mask or face shield
Distance of three feet from everyone
Contact precautions
dispose of PPE in a sealed bag
Limit use of unnecessary equipment
Limit transportation
Wear gown if needed
Wear gloves
Private room
Airborne precautions
After care
Discard hazardous trash
Dispose of PPE in a sealed bag
During care
Limit unnecessary contact with medical equipment
Limit transport
Before care
Wear a form of respiratory protection such as a mask
Wash hands
Isolation with specific room settings