Sound waves to break up the stones, using surgery to remove the very large stones, passing a small needle through the ureter to remove stones, if the stones are caused by a malfunction in the thyroid then it can have a surgery
Ketoconazole, mitotane and mtyrapone can be taken to reduce the amount of cortisol produced
Fatigue, nausea, vomiting, headaches, muscle aches, high blood pressures, low potassium and swelling
Voluntary Muscles
Chemical Energy
Mechanical Energy
40% of Body Weight
Voluntary actions
Arm, Leg, Spinal, and Abdominal movement
Floating topic
Break Down Food
Heart Attack
Automated External Defibrillator (AED)
Heart beat
Electric shock
Reestablishes an effective heart beat
Makes the heart start beating
Thrombolysis
Radiation
Clears blood clots
Space for blood to flow
If the person does not smoke or drink and has a healthy diet/lifestyle.
When the flow of blood to heart is blocked
Less oxygen gets delivered to the heart.
Heart Tissue to die
Extra fat or cholesterol blocking the vessels
Left Ventricle
Gets sent here do it can get to rest of the body
Left Atrium
Blood is Oxygenated in the lungs it is brought here by the pulmonary veins
Right Atrium
Low Oxygenated blood from the body using Systemic veins
Right Ventricle
Gets sent here so it can be sent to the lungs using Pulmonary Arteries
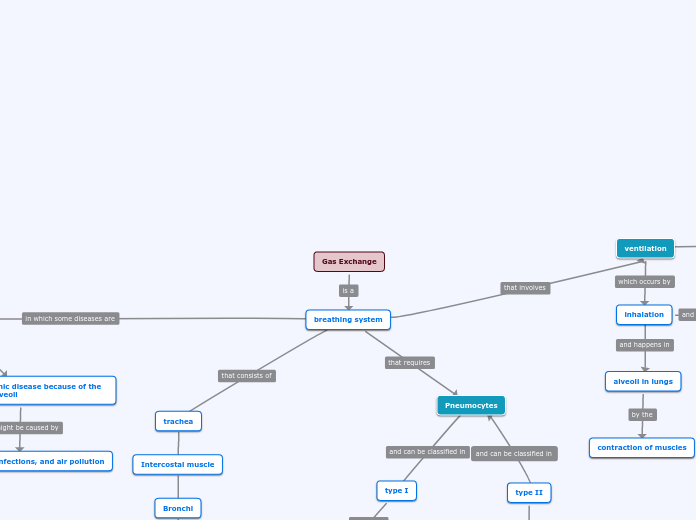
Airways
Asthma
Medicines such as fluticasone, budesonide and beclomethasone
Inhalers
Used to relax airways and allow air to travel easier to and out the lungs
Obtained from having things such as dust and pollen in your airways, or having your airways narrow and produce more mucus. usually obtained from bad environments or at birth
Trachea
Carries air from the Larynx
Larynx/Pharynx
Pharynx carries water, air and food through your throat
Larynx Carries the oxygen from the Pharynx to the Trachea
Mouth/Nose
The Sinuses
Temperature and Humdidity of the air you breath in
Hollow Spaces In the Skull which open up to the nasal cavities
Bring air from the outside of your body
Lungs
Alveoli
Emphysema
Can not be cured, but symptoms can be lowered with the use of antibiotics and inhaled steroids such as beclomethasone dipropionate, budesonide and ciclesonide
Coughing, hard time breathing, chest pain and tightness, and wheezing, symptoms can range from mild to extreme depending on the person
The alveoli starts breaking down and they small holes inside them become larger than normal, causing a hard time for the oxygen and carbon dioxide to be separated
Separates oxygen and carbon dioxide and oxidates blood cells
Bronchioles
Branches off from bronchi and sends air from and into the alveoli
Bronchi
Carries air from and to your Bronchi
Technologies
Dual Energy X Rays
Densities of bones
Scans Bones which can detect Osteoporosis
Romosozumab
Strengthen bones
Ligaments
Fibrous Connective Tissue
Connecting's bones to each other. Holds all the bones to keep them stable
Tendons
Connecting bones to muscles. Holds the bones and muscles together
Cartilage
Is a flexible tissue that keeps joint motion fluid by cushioning bones against impact and by cushioning bones against other bones/joints
Elastic Cartilage
A type of cartilage that provides both strength and elasticity to certain parts of the body
Hyalin Cartilage
Hyaline Cartilage has a smooth surface and is the most common cartilage. It has closely packed collagen fibers, making it tough but slightly flexible. Allows tissues to slide/glide more easily, as well as providing flexibility and support
Fibrous Cartilage
Fibrocartilage is the toughest of the three types of cartilage, it contains dense bundles of fibers. This makes it perfect to provide support and rigidity
Connective Tissues
Central Sulcus
Temporal Lobes
Creating and Preserving both conscious long term and short term memory. It is also related to
The Cerebrum
Right Hemisphere
Controlling Movement on the Left Side of the body
Left Hemisphere
Controlling Movement on the Right Side of the body
Parietal Lobes
The Upper-Back portion of the brain. It is used for Sensory Processing and Navigation/Control
Superior Parietal Lobul
Spatial orientation and visual input as well as sensory input from one's hand.
Somatosensory Cortex
Receiving and processing Sensory information from across the body.
Angular Gyrus
The Processing of Numbers and Words, and other Complex language functions
Frontal Lobes
The most anterior and front part of the brain. It is used for Higher Cognitive Functions, Voluntary Movement, and Expressive Language.
Occipital Lobes
Visual Perception, this includes colour, form and motion
Cured With Technology
Blood tests and oral fluid
Insulin pump
Usually placed near the hip
Pumps insulin into your liver and helps lower sugar levels
HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus)
Darunavir, Fosamprenavir, Indinavir, Nelfinavir, Ritonavir
The CD4 or T Cells to be killed. As the virus continues to kill these cells your immune systems weakens.
AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Ayndrome)
Diabetes
Body to be unable to manage sugar intake
Hyperglycemia
The Immune System. It causes dysfunction by allowing pathogens to spread in Diabetic Patients
Your Pancreas doesn't make enough Insulin for your body. This is usually due to genetics
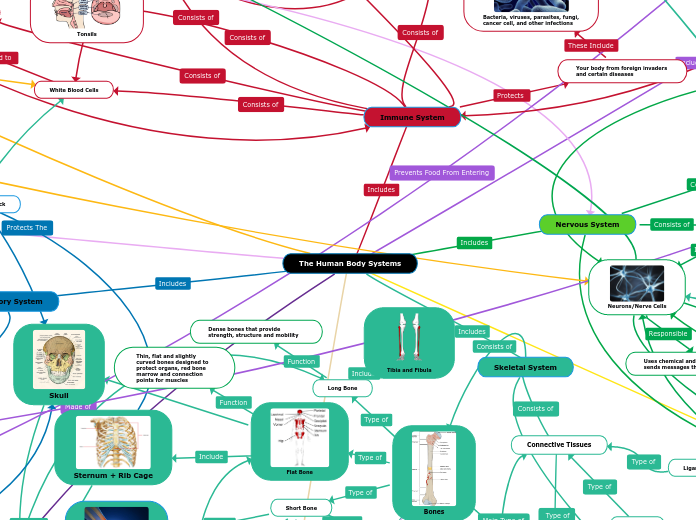
Prevent harmful substances from entering your body using protective proteins. It is a natural filter which kills dangerous bacteria
Mucus
Tonsils
Trap Germs and infections through the mouth and nose.
Protects your body from the outside. Prevents germs and bacteria from entering the body. Produces oils and secrets other important cells
The Lymphatic System
Lymphocytes
T Cells
Killing infected or cancerous cells. They direct the immune System by helping B cells create Antigens.
B Cells
Antibodies
Types of proteins which attack antigens and remove them from the body
Antigens
Toxins or foreign substances which are killed by Antibodies
Lymph Nodes
Carry Lymphocytes that fight infections. They are located throughout the body
The Spleen
White Blood Cells
Fight infections by traveling through the blood stream. They produce Anti-Bodies to kill organisms
Single-Celled Organisms
The Human Body Systems
Digestive System
GERD
Minimally-invasive treatment
Is cut into small holes
Are placed inside
Surgery without cutting too much skin
Transoral incisionless Fundoplication
Is let in your stomach through the esophagus
Surgury is used
82% Success Rate
A Portion of the stomach around the Esophogus
Antacids
Heart Burn
When Stomach acid flows up the espophogus
Acid Reflux
Gastroesophageal reflux disease
Accessory Organs
Pancrease
Enzymes
Gallbladder
Bile
Liver
Salivary Glands
Chemical digestion of food by secreting enzymes
Alimentary Track
Intestines
Small Intestines
Nutrients
Carbohydrates and fats
Protiens
Vitamins/Minerals
Further digest food
Large Intestines
The remaining Food (without nutrients) into feces
Stomach
The food using enzymes and gastric acid
Pharynx
Sensory Receptors
Involuntary Swallowing Reflex
Epiglottis
Choking
The Uvula
Saliva
Nasopharynx
Air Flow into your lungs
Fauces
A Passageway
The Throat
Esophogus
Esophogael Sphincter
Lower Esophogael Sphincter
Muscular valve
When there is not food entering the esophogus
When food is passing through
Upper Esophogeal Sphincter
Mouth
Tongue
Food into the pharynx/esophogus
Is to undergo active digestion of food and absorption of nutrient
Skeletal System
Osteoporosis
A Cure
Fractures and Broken Bones, Mostly common for Carpal Bones and your spine
Disease that weakens bones to the point where they break easily
Calcium, Vitamin D/K, and Magnesium
Bone Marrow
Yellow Bone Marrow
Fat, cartilage, and bone cells
Red Bone Marrow
Stem Cells
Specific instructions
The potential to become all other types of cells
Renew themselves over a period of time
First Cells in your cell linage
206 Bones in the Human Body
Flat Bone
Skull
Sternum + Rib Cage
Thin, flat and slightly curved bones designed to protect organs, red bone marrow and connection points for muscles
Short Bone
Patella
Short bones, usually containing spongy material, help provide stability and small movement adjustments to wrists and ankle joints
Tarsal Bones
Carpal Bones
Long Bone
Dense bones that provide strength, structure and mobility
Tibia and Fibula
Respiratory System
Higher Respiratory Track
Lower Respiratory Track
Respiration muscles
Abdominal muscles
Helps keep diaphragm and lungs in place, while also helping the diaphragm to contract and expand
Diaphragm
When diaphragm contracts, it creates a vacuum which sucks air from the outside into your respiratory system, and when it stretches it pushes air back out of your respiratory system
Nervous System
Parkinson's disease
Deep brain stimulation is used to deliver electrical impulses in the substantia nigra which disturb abnormal behaviors made from Parkinsons
Can not be cured but physiotherapy and medicines such as levodopa and carbidopa can lower symptoms
shaking, stiffness, uncontrollable movement, difficulty speaking and loss of balance and coordination
Loss of nerve cells in the substantia nigra which is responsible for dopamine and muscle controls
Central nervous system
Neurons/Nerve Cells
Interneurons
Relay interneurons
Local interneurons
Uses chemical and electrical signals to sends messages throughout the body
Spinal cord
Paralysis
There is no cure to paralysis since the spinal cord cannot repair it self, and usually an amputation is needed
Amputation
Amputation is the removal of a body part and is usually replaced by prosthetic
Damage to spinal cord from an injury, event or birth defect called spina bifida
Loss of ability to move some or all of your body
connects everything in the nervous system
Brain
Four Interconnected Lobes
Controlling Emotions, Memory, Touch, Motor Skills, Hunger, Breathing, and the other senses in our body. The Brain controls every muscle, bone, organs, and body system.
Peripheral nervous system
Autonomic nervous system
Parasympathetic nervous system
The top and bottom of the spinal cord
Responsible for conserving energy to complete involuntary actions and drives the "rest and digest" conditions in quiet situations
Sympathetic nervous system
The center of the spinal cord
Responsible for increasing heart rate, body temperature, blood pressure and creating sweat in stressful situations driving the "fight or flight" conditions
Regulates involuntary actions such as breathing, heart rate, blood pressure, respiration, digestion, body temperature and sexual arousal
Somatic nervous system
Motor neurons
Moves information from the brain and spinal cord to the fibers and muscles in the body
Sensory neurons
moves information from the body to the Central nervous system
connects the central nervous system to the muscles throughout the body
Muscular System
Myopathy
Braces
Bones
The strengthining of Bones
Joints
Proper Muscle Function
Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
Electromagnetic signals that are produced by the atomic nuclei inside teh molecules of a muscle tissue
Scan Tissues
Muscle Diseases
If it affects the Heart/Cardiac Muscles
The Heart struggling to work
Heart Failure
Muscle Weakness
Dysfunction of muscle fibers
Struggle and stiffness of muscles
Cardiac Muscle
The Muscles in the heart
Skeletal muscles
Opposing Pairs
Antagonistic Pairs
Quadriceps and Hamstrings
Biceps and Triceps
Muscle Relaxes
Antagonist
Muscle Contracts
Agonist Muscle
Tissue that is attached to bones and allows movement
Striated Muscles
Stripped Appearance
Smooth muscles
Myosin Myofilaments
In Voluntary Muscels
Under our control and are involuntary actions
Layered sheets
Internal Organs and Structures
Walls of Vessels
Walls of Internal Organs
Immune System
Your body from foreign invaders and certain diseases
Bacteria, viruses, parasites, fungi, cancer cell, and other infections
Are organism which lives inside a host organisms (Human Body) Recieve energy by feeding on the internal organs of a host
Can live outside of a host (Air, Surfaces) Thrive and stay alive by affecting other cells, making copies of its self.
Found almost everywhere in the world, there are good types and dangerous types of bacteria
Integumentary System
Keratin
Type of protein that makes up your hair, skin and nails
Nails
Nails start growing at root under the cuticle (also known as nail bed) and when new cells grow, it pushes older cells forward which allows our nails to keep regrowing. When the cells leave the cuticle they die and harden turning into nails
Protect the sensitive tips of our fingers and toes, and help use do small things such as pick up small objects scratching and untying knots
Hair
Protects against external factors, creates sebum, apocrine sweat, and pheromones and helps regulate body heat by trapping heat
Pheromones are a type of chemical which hair creates in other animals of the same species which helps in mate finding and looking attractive
Sebum, also known as natural oils, protects, moisturizes and coats your skin
Skin
Skin cancer
Cryosurgery
Is Frozen
Liquid Nitrogen
Skin is cut off
Cancer from Spreading
Overexposure to sunlight, usually because of a low amount of body oil, which causes the UV rays from the sun to damage to DNA in the skin, causing abnormal cells to grow. These cells can divide in a disorganized manner which creates a mass of cancer cells
Small smooth waxy bumps on the face, ears, and neck. Flat pink/red or brown colored lesion on arms and/or legs. Areas on the skin look like scars. Sores that look crusty and bleed often
Epidermis
Protects the body from harm such as UV radiation, bacteria, viruses, fungi, parasites and chemicals.
Melanocytes
Creates melanin which is a group of pigments which provide us with our skin colour
Basale
Deepest layer of the epidermis, creates keratinocytes which when exposed to sunlight helps create protein, lipids and vitamin D
Granulosum
Uses a chemical called glycolipids to glue skin cells together
Lucidum
Only present in thicker layers of skin such as palms and soles
Corneum
The topmost layer of skin, thickness varies and it plays the first line of defense against other organisms
Hypodermis
Located on the bottom and connects the skin to the bones and muscles
Macrophages
Macrophages are a type of white cells which fight off unknown organisims such as fungai, viruses and bacteria when the tissue is injured
Adipose
Commonly known as body fat and is used to store excess nutrients as fat and is also used as a type of shield
Connective tissues
Cells, fibers and gel like substance
Supports organ structure and helps connect other tissues and organs in the body
Made from fibroblast cells as they help maintain the structural framework of tissues
Dermis
Protects body, supports epidermis, provides elasticity to the skin, a sense of touch since the nerves are located in the dermis, and heat
Hair folicles
Vitamin A, Vitamin B, Vitamin C, Vitamin D, Vitamin E, iron, zinc and proteins
When the hair is unable to push through the skin, usually due to Fungai or infections, a red or white pimple grows around the hair follicles
Tunnel shaped structure in the dermis and epidermis which grows hair in the bottom of it, this hair then pushes up through the skin
Telogen, also known as the resting phase, is when the old hair falls out and the new hair begins to grow from the same follicle, this takes around 2-4 months. These phases repeat constantly
Catagen, also known as the transitional phase, is when the growth slows down and the follicles shrinks, usually lasts 2-4 months
Anagen, also known as the growth phase, is when the hair starts growing from the root and usually takes 3-7 years
Oil and sweat glands
everywhere in the body, mostly found in the forehead, arm pits and palms
Disposes water with salt to lower body temperature, as the water in the sweat evaporates it cools the body down since it takes it heat
Excretory System
Urethra
Tube which carries urine out of the human body, its a long tube which passes through the penis in the male body and also carries semen, while in the female body it is a small hole located abou the vagina
Bladder
Connected by both ureters and is made of smooth muscles that expand and compress to store urine and push it out of the urethra
Ureters
Right ureter
Left ureter
Tubes that propel urine from the kidneys into the bladder, usually 20-30cm long and 4 mm in diameter
Kidneys
Kidney stones
Percutaneous Lithotripsy
Drinking lots of water, pain relievers and medical therapy for small sized stones
Severe pain, nausea, vomiting, fever, chills and blood in your urine
When someone drinks too little or too much water, exercise too little or too much, obesity, weight loss surgery and eating foods with lots of sodium or sugar. On rare occasions it can be caused by a malfunction in the thyroid gland
When the many pathways in the kidney (mainly uterus) get blocked by clumps of sodium or salt causing the kidney to malfunction
Right kidney
Left kidney
Nephron
Simple two step process where the glomerulus filters your blood, and the tubule returns the needed substances back into the blood while also removing the waste creating urine
Capsule
Protects the kidney from the outside and helps support the kidneys mass
Pyramids
Carries urine from the nephron to the calyx before it reaches the baldder
Renal cortex
Protects the inner structure of the kidney, mainly the pyramids and nephron
Calyx
Collects fluids from the nephron before it passes through the bladder, extra fluids become urine in here as well
Removes wastes and extra fluids from the body, they also remove acid created by your cells and help maintain your calcium, phosphorus, sodium and potassium
Endocrine System
Hormones
The bodies chemical messenger
Hypothalamus
Pituitary gland
Posterior pituitary gland (back side)
Cushing disease
Tumor
Pituitary radiotherapy
Radiation from an external device
The DNA
The human skin and bone
Severe fatigue, muscle weakness, depression, anxiety, loss of emotional control, high blood pressure, headaches and infections
Noncancerous tumor on the adrenal which gets worse without proper treatment
Occurs when your body produces too much cortisol
Growth hormones
Adrenal (produces adrenaline) and Cortex (produces cortisol)
Anterior pituitary gland (front side)
Signals to the mammary glands to produce milk
During birth or labor
Kidney function
Medial lateral
Lateral
Movements, pressure, vibrations and spatial awareness
Medial
Decision making
Pervinitluclar
Aging of the human body
Parasagittal plane
Ventromedial
Controls fear, thermoregulation and sexual activity
Mammillary
Controls memory, mainly recollective memory which begains with hippocampus located in the brain
Tuberal
Controls the feeding impulses
Supraoptic
Create and secrete the peptide hormone vasopressin, or antidiuretic hormone, responsible for controlling the body's blood pressure, sodium regulation and kidney function
Glands
Female ovaries
Females
Responsible for creating egg cells called ova occytes
Adrenal
Produce adrenaline, aldosterone and cortisol
Stress hormone which increases sugars in the bloodstream and enhances your brains use of glucose and substances that repair tissues
Steroid that plays the main role in regulating the slat and water in the body which effects the blood pressure
Triggers the bodies fight or flight response and causes the air passages to dilate and provide more nutrients and oxygen to the bodies muscles
Thyroid
Plays a huge role in the development of the human body by making sure the thyroid hormones are steady in the bloodstream
Male testes
Only found in males
Creates sperm cells and a hormone called testosterone responsible for maturity and puberty
Circulatory System
Heart
4 Chambers
Left Side
Right Side
Blood Vessels
Arteries
Systemic Arteries
Blood from the Left Ventricle to the rest of the body
Pulmonary Arteries
Blood from the Right Ventricle to the lungs so it can be oxygenated
Oxegenated blood from the heart to the rest of the body
Veins
Systemic Veins
Low Oxygenated blood from the body to the right atrium
Pulmonary Veins
Blood from the lungs to the left atrium of the heart
Unoxygenated blood from the body to the heart
Capillaries
Sinusoid Capillaries
Allow for exchange of larger molecules, even cells since they are a type of capillary vessels with a wider diameter, found in endocrine glands, bone marrow, lymph nodes, spleen and liver
Fenestrated capillaries
Blood vessels with tiny pores, or holes, which allow larger molecules and proteins to move from your blood into organs, usually found in kidneys, intestines and pancreas
Continuous capillaries
The smallest blood vessels, responsible for connecting your arteries to your veins and support your brain, endocrine system, kidneys, lungs and the small intestines