To help management make decisions and serve the needs of bankers/investors outside of the business.
Gathering any financial information about the activity of the business
Uses records to provide evidence of purchases
Classifying different financial data, rearranging the data for financial analysis, and summarizing the data in a neat, readable way.
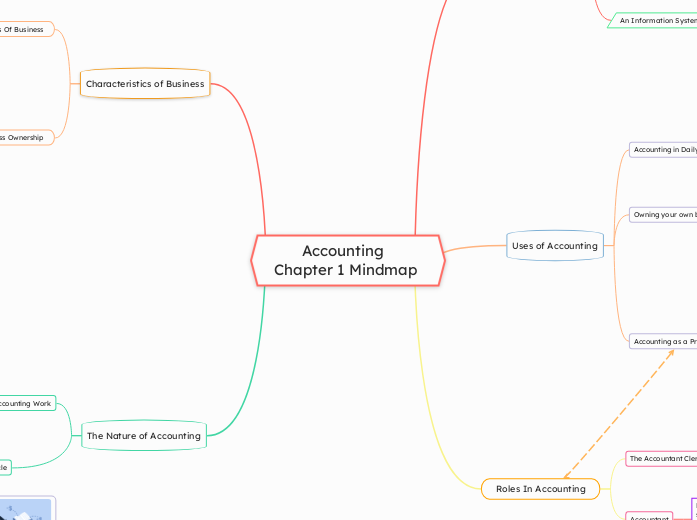
Accounting
Chapter 1 Mindmap
The Nature of Accounting
The Accounting Cycle
Outer Circle - Ongoing intermitten activities
Inner Ring - Activies Done Annually
Categories of Accounting Work
Miscellaneous Activities
Activities that occur at unpredicted times (accounting employee resigns, concerns over bank loan size, etc.)
Periodic Accounting Activities
Activities that occur at regular intervals (weekly, biweekly, monthly)
Routine Daily Activity
Activities that occur the same way every day (Processing bills, preparing cheques, daily banking, etc.)
Characteristics of Business
Forms of Business Ownership
Corporation
Owned by Shareholders
Partnership
Two or more people own the business
Sole Propietorship
Single owner of the business
Types Of Business
The Non-Profit Organization
Carry out social needs without
trying to collect a profit
Manufacturing and Producing Business
Producing: Collect and sell raw materials
(e.g. farms, mining)
Manufacturing: Buys raw materials and
converts them into products (e.g. car companies)
The Merchandising Business
Buys and Resells goods at a
higher price (e.g. supermarkets)
The Service Business
Sells a service to people
(e.g. salon, car wash)
Roles In Accounting
Accountant
Requires more education and experience, making sure the correct data is put into the accounting system, analyzing financial statements and making reports for management.
The Accountant Clerk/Book Keeper
The work of an Accountant Clerk is known as bookkeeping, including ensuring transactions are properly recorded, recording account entries in books of account, making many types of payroll records, and carrying out all bank transactions. Accountant clerk's are usually more entry level accountants.
Uses of Accounting
Accounting as a Profession
When becoming a professional accountant, there are entry-level and high-level positions. People filling these spots can have little to no training or multiple years of experience. Accountants get training from high school, college or university, and gather on-the-job experience to be prepared.
There used to be 3 jobs you could get as a professional accountant, however it is now merged as one: Chartered Professional Accountant (CPA).
Management/Institutional Accountant - Works for large companies, the government, banks, universities, etc.
Public Accountant - Works for the general public (anyone who pays them), doing an important task called Auditing. An audit is the testing of records and procedures of a business so that they can express their opinions on their financial statements.
Owning your own business
When creating your own business, a business owner has to deal with banking, keeping track of accounts payable and recievable, keeping accounting records for the government, making income tax statements, and possible preparing payroll and payroll deductions.
Accounting in Daily Life
Having accounting knowledge can prove useful in daily life, as it can help when dealing with personal business affairs like personal budgeting, personal financial records, and preparing income tax return. It also allows you to take any business opportunities
What is Accounting?
An Information System
Preparing Financial Reports
Rearranging, summarizing, and classifying
Preparing/Collecting Records
Gathering Financial Information