1. One type of cell division is called
2. During meiosis, a ladder of parallel threads is visible and is called:
3. Has a first division cell called:
4. Also has a second round called:
5. Produces 4 Daughter Cells.
6. Set of Maternal and Paternal cells called:
7. Homologous pair exchange the same with other by the process of.
8. Forms a homologous structure called.
9. Steps that build the mitotic spindle it interacts with.
10. The centro some consists of.
11. The 23rd pair which defines if its male or female.
12. The set of 2 pairs of 23 chromosomes create a
13. A Zygote is a type of
14. Diploid cells are a
15. Are involved in
16. A type of Asexual reproduction is
17. Are produced by.
18. Number is half
19. Is a
20. Sets of chromosomes form a
21. An individuals genome is created by its parents through
22. Has Stage called
23. Are both series of changes in a
24. Has a type of cycle that occurs in those plants and algae called
25. Are in different forms such as a
30. Contain
31. Are the specific code for the
32. Are located in a specific place called
33. Are studied through
34. Studies
35. And
36. Is one part of the
37. Cytokineses and begins the progression of cleavage
38. Animal and some aleged cells undergo cytokineses and begin the progression of cleavage.
39. During the cell cycle, the chromatin condensation changes
40. Cell cycle's mitotic and meiotic phrases are stimulated
41. cell cycle's first phase
42. Cell cycle's fourth phase
43. Cell cycle's third phase
44. Cell cycle's second phase
45. System in the cell cycle that directs sequential events by specific chemical signals
46. Groups of protein that regulate the progression of cells
47. part of the cell cycle that divide into five stages
48. second phase of mitosis
49.
50. third stage of mitosis
51.
52. fourth stage of mitosis
53.
54.
55. first phase of mitosis
56. cells undergo reproduction and
57. cell division is stimulated by
58. growth factor is controlled by
59. contribute to
60.
61.
62.
63.
64.
65.
66.
67.
Cell Division
Growth Factor
cell division is stimulated by
Malignant Tumor
growth factor can also cause the grow of
Metastasis
one example of a malignant tumor is
Benign Tumor
Growth factor can cause the grow of
Anchorage Dependence
Contributes to
Density Dependence Inhibition
growth factor is controlled by
Cell Cycle
Cell division is part of the
Mitosis
part of cell cycle in which nuclear division in eukaryotic cells conventionally divided into five stages
Telophase
Anaphase
Metaphase
Second phase of mitosis
Metaphase Plate
Prophase
First phase of mitosis
Cell Plate
Mitotic Spindle
Cyclin
Mitotic (M) Phase
Cell cycle's first phase.
G1 Phase
Cell cycle's second phase.
S Phase
Cell cycle's third phase.
G2 Phase
Cell's fourth phase.
Cytokineses
cell cycle phase followed by mitosis
Cleavage Furrow
Animal cells undergo cytokinesis and begin the progression of cleavage
Maturation Promoter Factor
stimulates the mitosis and the meiosis phases of the cell cycle.
Cell Cycle Control System
system in the cell cycle that directs sequential events by specific chemical signals
CDKS
Groups of proteins that regulate the progression of cells
Chromatin
During the cell cycle, the chromatin condensation changes
Transformation
In cell division, cells undergo reproduction and
Meiosis
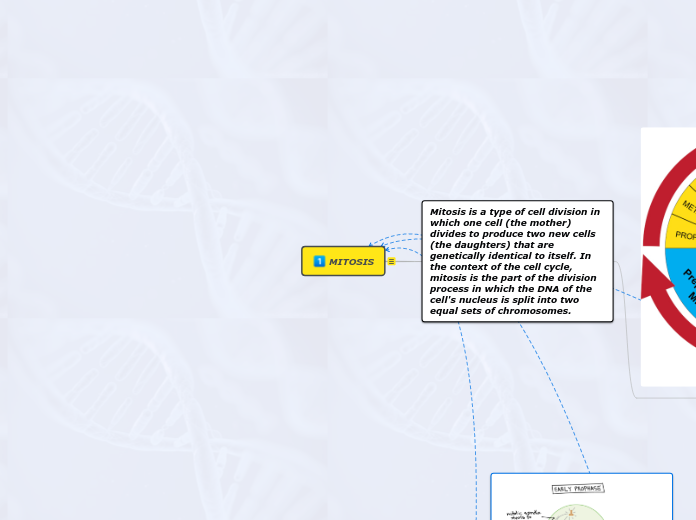
One type of cell division is called.
Chromosomes
produces 4 daughter cells with half number of.
Centromere
Sister Chromatids
Karyotype
Kinetochore
Recombinant Chromosomes
Gamete
Haploid Cell
Genome
Sexual Reproduction
Fertilization
Life Cycle
Alterations of Generations
Asexual Reproduction
Binary Fission
Clone
Zygote
Diploid Cell
Somatic Cell
Sex chromosome
Centrosome
Aster
Homologus Chromosomes
Pairs that are similar in length, gene position, and centromere location.
Crossing Over
When homologous chromosomes exchange genetic material it is called
Chiasmata
Crossing over, forms a structure between a pair of homologous chromosomes called
Genes
Genetics
Heredity
Variation
Locus
Traits
Allele
Meiosis II
Round of meiosis where sister chromatids separate and 4 haploid daughter cells are produced
Meiosis I
Round of meiosis where homologous chromosomes separate
Synaptonemal Complex
Protein structure that forms between homologous chromosomes during meiosis and is thought to mediate chromosome pairing, synapsis, and recombination.