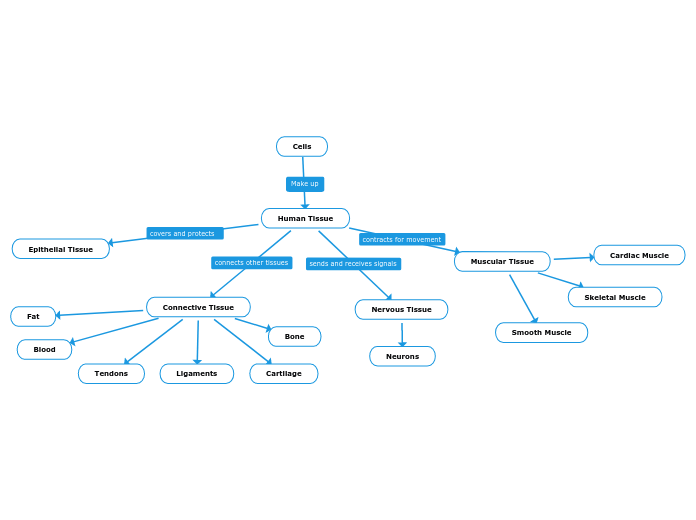
Body Tissues
Epithelial
Simple
Secretes and reabsorbs water and small molecules and lines kidney tubules and glands, looks like cubes
Exchanges gases and found in the lungs, flat like a pancake
Absorbs nutrients, produces mucus and lines most digestive organs, looks like columns
Stratified
Cuboidal
Secretes water and ions and lines ducts of sweat glands, looks like cubes
Squamous
Protects against abrasion and is found in outer layer of skin, mouth, vagina, flat like a pancake
Columnar
Secretes mucus and lines the epididymus, mammary glands, larynx, looks like columns
Nervous
The nervous system consists primarly of cells that are generating and transmitting electrical impulses througout the body. It sends and receives messages throughout the body. Nervous tissue contains a cell called a glial cell which does not transmit electrical impulses. Its function is to react to stimuli and reactive impulses to various numbers of neutrons. It is found in the brain and spinal cord.
Muscle
Cardiac
Cardiac muscle tissue is only found in the heart. Individual cells are much shorter than skeletal muscle fibers, they only have one nucleus. Arranged parallel to each other. Cells are short and blunt-ended with gap junctions between ends of adjoining cells. It has involuntary movement. It is branched and blue.
Skeletal
Skeletal muscle tissue connects to tendons, which attach to bones. It connects to tendons, which attach to bones. Individual fibers are thin cylinders too small to be seen with the naked eye. Arranged parallel to each other. Its function is to move the skeleton and contract. It has voluntary movement. It is everywhere connected to every bone in the body.
Smooth
Smooth muscle tissues surrounds hollow organs and and tubes, including blood vessels, digestive tract, uterus, and bladder. The slim cells are much smaller than skeletal muscle cells. Only have one nucleus, like cardiac muscle. Aligned roughly parallel to each other. Cells are tapered at both ends with gap junctions between adjacent cells. Its function is to digest and contract internal organs. It has involuntary movement.
Connective
Specialized
Adipose
It stores fat in the form of energy. It is found in everything including beneath the skin, around joints, padding the kidneys and other internal organs.
Cartilage
It is rigid connective tissue that provides a supportive framework. It lacks a vascular system so it heals slowly. It is found in the ends of bones and in the ear.
Bone
It's the most rigid connective tissue, with deposits of mineral salts and collagen within the matrix. Supports body and forms muscle attachments and the site for blood cell formation. It is found everywhere in your body.
Blood
It is composed of cells and suspended in a liquid matrix called plasma. Produced in red marrow. Transports substances throughout the body. It is found everywhere in your body.
Fibrous
Loose Connective Tissue
It forms delicate, thin membranes throughout the body that bind body parts together such as skin and underlying organs. It is found throughout the body.
Dense
It consists of densely packed collagenous fibers and is very strong but lacks a good blood supply. It is part of tendons, ligaments, and aponeuroses (very flat tendon).
Elastic
It surrounds internal organs that can expand and contract internal organs.
It is found in the stomach, lungs, intestines and bladder.
Reticular
It allows you to filter blood cells. It surrounds lymph nodes and the spleen.