transmembrane protein
2 Acetaldehyde
Lactate
Alcohol Fermentation
Lactic Acid Fermentation
Aerobic Cell Respiration
Glycolysis
Phases
Energy Payoff
4 ATP
2 NADH
Energy Investment
2 ATP
Pyruvate
Glucose6P
Fructose6P
Fructose 1,6 Bisphosphate
Pyruvate Oxidation
Enters Mitochondria
Oxidizes
Acetyl CoA
Oxaloacetate
Citrate
NADH
Oxidative Phosphorylation
Anaerobic Fermenation
Alternate Splicing
Spliceosome
Floating topic
Ligase
Okazaki Fragments
Lagging Strand
Leading Strand
Primase
SSB
Topoisomerase
Replication Bubble
Helicase
Replication Fork
ORI
Dispersive
Semiconservative
Conservative
Messleson and Stahl
DNA Replication
DNA
double-stranded
bases
phosphate group + sugar
mitosis
metaphase
anaphase
telophase
prophase
2 diploid daughter cells
chromosomes
genes
genetic mutations
silent
missense
frameshift
meiosis
4 haploid daughter cells
meiosis II
meiosis I
chromosomes separate
sister chromatids separate
cells
somatic
diploid
gametes
egg
sperm
haploid
Collagen
Albumin
Casein
Insulin
Amylase
Secretion
Other Destinations of Proteins
Peroxisomes
Nucleus
Golgi
Back to ER
Vesicle
Glycoprotein
Stop Codon
Release Factor
Peptidyl
Transferase
Peptide Chain
Large Ribosomal
Subunit
Initiation
Factors
f-Met
Small Ribosomal
Subunit
Met
GTP
Amino Acid
Codon chart
tRNA
Template Strand
Termination
Pre-mRNA
5' Cap
RNA Splicing/ DNA Processing
Exons
Introns
3' PolyA tail
Elongation
RNA Synthesis
Promoter
Transcription Factors
RNA Polymerase (RNAP)
Initiation
RNA Polymerase II (RNAPII)
Eukaryotes
Prokaryotes
Translation
Transcription
Proteins
Flow of Genetic information
Concept Map 3
Phosphatase
cAMP
ATP
Adenylyl Cyclase
Ions
Cellular Response
Tyrosines
Phosphate Group
Kinase
Polypeptides
Enzyme
G Protein
Ion Channel
Receptor
Tyrosine Kinase
Receptor
G Protein Linked
Receptor
Protein
mRNA
Genes
Hormone receptor complex
Steroid Hormone
Intracellular Receptor
Membrane Receptor
Receptor
Signal Molecule
Paracrine Signaling
Long Distance Signaling
Local Signaling
Synaptic Signaling
Plasmodesmata (Plant Cells)
Gap Junctions (Animal Cells)
Eukaryotic Cells
Signaling
Physical Contact
Cell Communication and Signaling
concept map 2
energy transfer
energy flow
energy pyramid
food chains
trophic levels
cellular processes
cellular respiration
photosynthesis
types of energy
eletrical energy
thermal energy
light energy
chemical energy
cell membranes
active transport
endocytosis
receptor-mediated
pinocytosis
phagocytosis
energy (ATP)
exocytosis
passive transport
facilitated diffusion
polar molecules/ions
pump
carrier
concentration gradient
osmosis
water tonicity
isotonic
normal
flaccid
hypertonic
shriveled
plasmolyzed
hypotonic
turgid
lysed
diffusion
small, non-polar molecules
Origins of Mitochondria and Chloroplasts
in Eukaryotic Cells
Endosymbiont Theory
Ribosomes
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Lysosomes
Golgi Apparatus
Cytoplasm
Mitochondria
Membrane
Vacuole
(Both have)
Chloroplasts
secondary structure
beta pleated sheets
alpha helices
tertiary structure
quaternary structure
Animal Cells
ECM
Plant Cells
Cell Wall
Chemical Evolution Hypothesis
Oparin's Bubble Hypothesis
Miller Urey Experiment
Origins and Initial Structure
of Cells
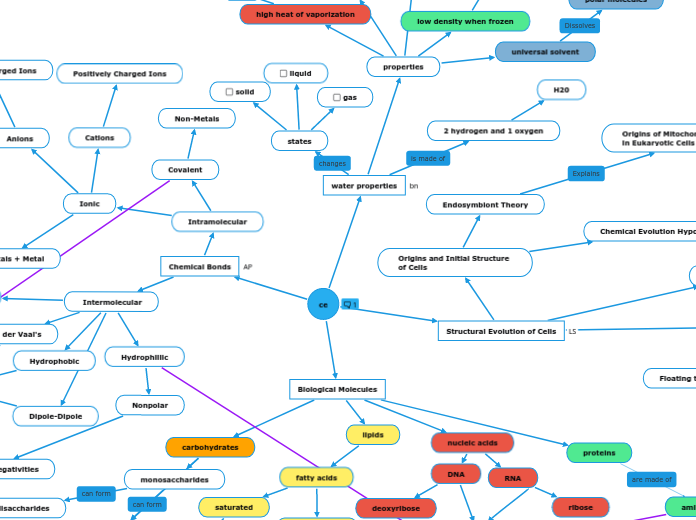
ce
hello
Structural Evolution of Cells
Biological Evolution
Replication of RNA
water properties
states
gas
liquid
solid
2 hydrogen and 1 oxygen
H20
properties
low density when frozen
water freezing @0 Celsius
water floats
universal solvent
polar molecules
high heat of vaporization
a lot of energy required to change from liquid to gas
high surface tension
hydrogen bonds
adhesion
capillary action
cohesion
high specific heat
a lot of energy is required to break hydrogen bonds between water
Biological Molecules
nucleic acids
DNA
nucleotides
nitrogenous bases
adenine
guanine
thymine
uracil
cytosine
deoxyribose
RNA
ribose
lipids
fatty acids
unsaturated
trans
cis
double bonds
saturated
single bonds
proteins
amino acids
primary structure
carbohydrates
polysaccharides
structure
cellulose
chitin
storage
starch
amylose
amylopectin
dextran
glycogen
monosaccharides
disaccharides
Chemical Bonds
Intramolecular
Covalent
Non-Metals
Ionic
Cations
Positively Charged Ions
Anions
Negatively Charged Ions
Non-Metals + Metal
Intermolecular
Dipole-Dipole
Hydrophillic
Nonpolar
Similar Electronegativities
Hydrophobic
Van der Vaal's
H-Bond
Polar
Differing Electronegativities