Conditions for and Impediments to Social Change
Values and Social Change in Canada
Capitalism/Classism
Source: Ricardo Levins Morales Art Studio. https://www.rlmartstudio.com/product/capitalism/
Wall Street
Capitalism contributes to a number of social justice issues and many activists spark social change because of this. Occupy Wall Street is one of many assemblies set on decreasing the gap between the top 1% of richest people and the other 99%. Greta Thunberg, a climate activist, goes after governments and organizations trying to mitigate climate change.
Climate Crisis
Alternative Environmental Paradigm
Theory: People need to encourage sustainability and interpersonal relationships. We need to put less of an emphasis on material wealth.
Dominant Paradigm
Widely accepted theory/worldview
Theory: People believe people need material wealth for future generations. “The end justifies the means” even if it means exploiting the environment.
Equality
Systemic Discrimination
Participation Rates
Percentage of women employed, typically lower than men
Feminism
Employment Equity Act
Act to increase equality in income distribution in 1996 between people of marginalized groups
Now Pay Equity Act to mitigate gender pay discrimination
Charter of Rights and Freedoms: Section 28 says men and women are equal under the law
Pluralism/Inclusiveness
Definition: Society should welcome and accept a variety of beliefs and opinions.
Singularity
Definition: All should act and think in the same manor.
Poverty and Affluence in Canada
Absolute I.I
Definition: Comparing demographics/groups of people
Wage Gap
In 1998, women made about 19% less than men on an hourly wage and in 2018, women made 13% less than men. This systemic discrimination can be attributed to a number of factors, for example, men often advance to higher positions where they do the exact same work as women, but get paid more. Maternity leave and inequality go hand and hand; companies can find ways to pay women less when they return from maternity leave. For example in R. V. Fraser, women in job-sharing were denied their pension despite the fact that men who had been suspended for misconduct had the option to buy-in and access their pension.
Source: Statistics Canada. (2019). The gender wage gap in Canada: 1998-2018. https://www150.statcan.gc.ca/n1/pub/75-004-m/75-004-m2019004-eng.htm
Public Policy Questions
Definition: Questions and discussions that social institutions take part in to see whether or not change in public policy needs to occur.
Example: Public policy around gov. compensation during COVID changed with the creation of CERB
Relative Income Inequality
Definition: Comparing quintiles
Lowest Quintile
LICO
In the past 20 years, the low income cut-off has increased by approximately $2000 in rural communities, $3000 in communities with 30,000-99,000 people, and $4000 in communities with 500, 000+. The difference in increase across the population categories is likely due to inflation and more concentrated populations in this area. The cost of living in cities and higher population areas in Canada tends to be higher as well which explains the $2000 difference between rural communities and 500,000+ areas.
Source: Statistics Canada. (2021). Table 11-10-0195-01 Low income cut-offs (LICOs) before and after tax by community size and family size, in constant dollars.
Welfare
The welfare monthly payment for basic needs in Toronto has increased by an average of $125 since 2001.
Source: Toronto. (2021). Monthly Ontario Works Amounts. Retrieved from Monthly Ontario Works Amounts – City of Toronto.
Disincentive
People believe that welfare disincentives people to work. I believe that this opinion is heinous because people that require welfare are absolutely not choosing to be on welfare so that they do not have to find a job. People on welfare typically have all odds stacked against them and it is unfair to assume that they are lazy. If anything, welfare should come with more services such as health care and child care so that people can get a job without worrying about mental health disorders and caring for children.
Functional Repurcussions
Definition: Outcome of welfare payments; people do not need to work (disputed).
Highest Quintile
In 1996, the highest quintile held 40.6% of total income. In 2017, the highest quintile earned an average of $179, 800, the top 10% had an average income of $135, 900, and the top 1% had an average of $381,300. This group of people can be considered modernizing elites and can influence social change by controlling stock markets, dictating the direction of marketing and businesses, and funding projects that align with their values.
90% of Canadians had an average income of $28, 000. This group of people have the power of numbers. Parts of this group are considered proletariats, a term coined by Karl Marx. Social change can be created by the masses, such as the Regina Riot, showing that both the highest and lowest quintiles have great potential for inciting social change.
Source: Statistics Canada. (2018). Education and occupation of highincome Canadians (statcan.gc.ca).
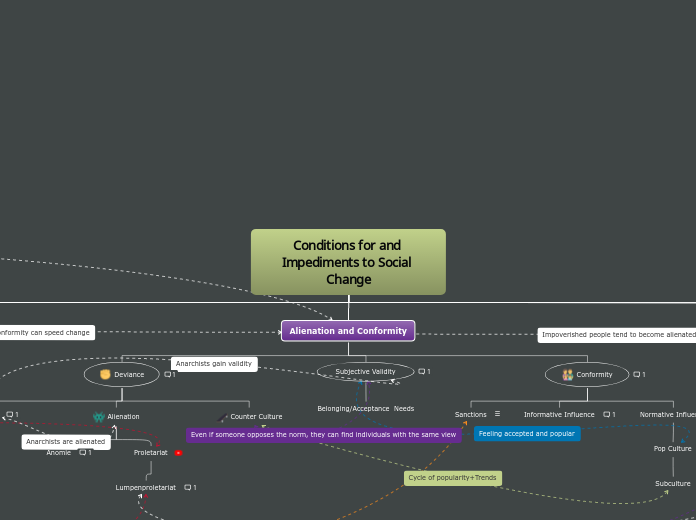
Alienation and Conformity
Conformity
Definition: When an individual's thoughts/beliefs/identity is shaped by society or a group.
Normative Influence
Definition: Conforming in order to be liked or accepted by a group.
Example: Teenagers' fashion sense
Pop Culture
Subculture
Informative Influence
Definition: Conforming based on the belief that others' behaviour is more correct than ours.
Example: The elevator experiment
Sanctions
Definition: Social control; way of enforcing conformity. Can be formal (ie. laws, government acts) or informal (ie. paradigms, social cues)
Subjective Validity
Definition: Social psychologists say that groups of people with similar beliefs and views gain validity and feel acceptance by belonging to a group.
Belonging/Acceptance Needs
Deviance
Behaviour that goes against the norm
Counter Culture
Alienation
Proletariat
Lumpenproletariat
Definition: Lowest "caste", typically unemployed, lowest members of the working class.
Anomie
Definition: Outcast
Anarchy
Definition: Rejecting government/authority including their sanctions and dominant paradigms.
Impediments to Change
Social Science Inquiry
Used to identify needs, social sciences look at areas that need social change and empowerment.
Participatory Research
Subject group participates to identify areas needing change.
Advocacy Research
Advocates participate on behalf of subject group.
Expense
Sometimes organizations cannot fund the projects that would create social change. Consequently, expenses are connected to capitalism and modernizing elites because people with money have more power and freedom to create social change.
For example, Doug Ford tried to implement changes to class sizes to decrease expenses in education. This change is met with walk-outs and protests because it goes against traditional values of good education and employing a variety of teachers.
Traditional Cultural Values
Traditional cultural values impede change when a population is not in the mood or is not ready to change their way of living. Often times, new technology creates challenges to traditional cultural values.
Routine/Norm
Modernity/Modernization
Social change is inevitable, society will modernize. Example: Technological revolution brought on by companies such as Apple, Microsoft, and Facebook
Traditional World View
Example: Older generations such as boomers and the silent generation reject or are reluctant to accept technology and modernization brought on by technological revolution. As a result, all iPads come with free e-books on how to operate iPads for seniors.
Challenge to World View
Group or organization attempts to bring social change that impacts working class
[Peasant] Resistance
Working class is not ready to give up their norms/way of life, they revolt in small ways such as stealing, bailing, not completing jobs
Populace Readiness
Populace readiness dictates how likely a population will be to acclimate to social change. For example, baby boomers are a large population that can influence markets and social changed based on what traditions and beliefs they will or will not forfeit. Gen Z is another important target market because they, along with millennials, tend to rule social media and technology. Social change spreads quickly if it can catch popularity over social media. Gen-Z and millennials have very strong morals codes but are more easily able to adapt to change whereas boomers tend to resist change.
Attitude of Populace
Educational Background
Theodore M. Newcomb conducted a study on women at a college based on their political views. He found that the political atmosphere of the school influenced most women's liberal views and that the lessons and atmosphere in their youth cemented these views later on in life.
Values established in youth
Question: Does the political party in power during a person's adolescence impact their political views and generation's readiness?
Opinion: I believe that naturally, people are influenced by the political atmosphere of their youth and whether they benefited from it or not. I think it is important to note that not just the country's political party is influential, but also the province's. The province dictates what teenagers learn and the political party can influence the curriculum. For example, with the Conservative Party being in provincial power during my high school years, my graduating class has seen how the party handles strikes, issues such as class sizes, and the attempted ban of phones. Many students did not benefit from the motions passed by the Conservative Party which is why I predict that much of my generation will hold liberal values when we are older. I also predict that the social change my generation creates will align with liberal values. Of course, there are many other factors that influence political identity, but I do think it is interest to compare the political views of people with the political atmosphere of their adolescence and how they did or did not benefit from it.
Political Views
Leadership & Roles of Elites
Leaders and elites contribute to social change by proposing new norms, setting trends, and gathering large followings. Large followings spread social change that they see leaders and elites demonstrating. A list of key leaders and elites relevant today:
Leaders
Justin Trudeau - Political
Kamala Harris - Political/Empowerment
Joe Biden - Political
Donald Trump - Political
Royal Family - Monarchy
Jeff Bezos - Business/Innovation
Elon Musk - Innovation
Alexandria Ocasio Cortez - Political
Barack and Michelle Obama - Political
Elites (In no order)
Music
Billie Eilish
BTS
Olivia Rodrigo
Justin Bieber
Taylor Swift
Ariana Grande
Drake
The WEEKND
Beyonce
Pink
Rihanna
Dua Lipa
One Direction Members
Kanye West
Entertainment
Kardashians/Jenners
Tik Tokers
Youtube Gamers
Beauty Gurus
Models
Oprah
Ellen DeGeneres
Dwayne Johnson
Ryan Reynolds
Will Smith
Angelina Jolie
Jennifer Aniston
Jennifer Lopez
Lin Manuel Miranda
Activism
Amanda Gorman
Greta Thunberg
BLM
Malala Yousafzai
Leaders and elites contribute to social change by proposing new norms, setting trends, and gathering large followings. Large followings spread social change that they see leaders and elites demonstrating. A list of key leaders and elites relevant today:
Modernizing Elites
Samuel N. Eisenstadt coins the term modernizing elites in 1973 and refers to a group of popular, influential people who incite social change. For example, "influencers" and the rise of the Tik Toker in 2020 lead to numerous modernizing elites such as Charli and Dixie D'Amelio, Addison Rae, and Bella Poarch. Typically, there is a group of modernizing elites backing a charismatic leader in order to create a trend or social change.
Politicians
Celebrities
Agents of the Law
CEOs/Corporations
Charismatic Leader
Magnetic, popular people that seem to exist in an extraordinary bubble tend to have the most power over the masses. Sociologist Max Weber theorized that these leaders are some of the most important people in sparking social change and have an end goal that they can impose on the population for bad or good. Some examples of these leaders are Adolf Hitler, Joseph Stalin, Martin Luther King Jr., and Opera Winfrey.
Subtopic
Grandiose Promise
Susceptible Population
A susceptible population is not a weak population, it is simply a group of people whose needs are not being met. In post-WWI Germany, people needed a strong front and they needed hope. Hitler exploited the desperation and promised many things which is how he created social change.