arabera Анеля Багдат 3 years ago
861
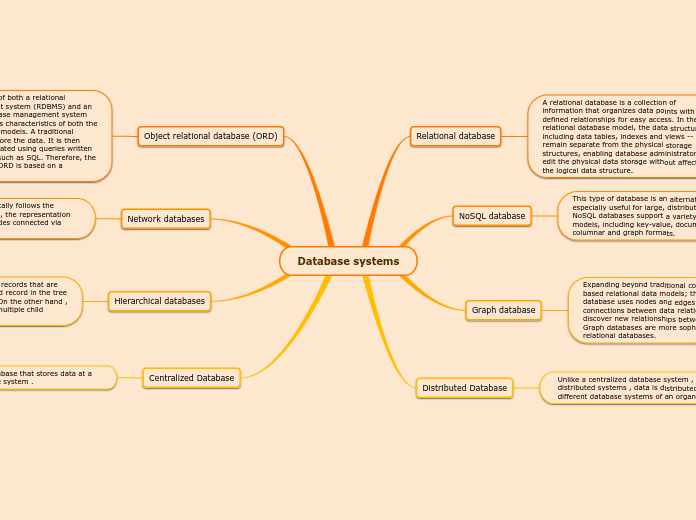
Database systems
Relational databases organize information with defined relationships, separating data structures from physical storage to allow seamless data management. NoSQL databases cater to large, distributed datasets with various data models like key-value, document, columnar, and graph formats.