arabera Cassandra Tekam 11 months ago
124
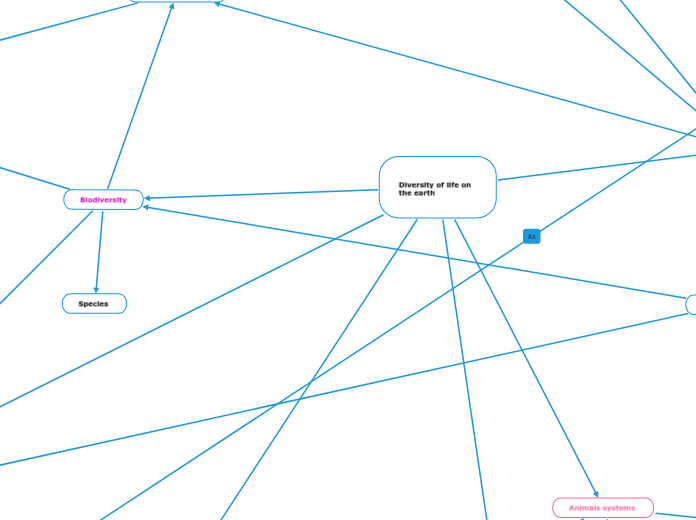
Diversity of life on the earth
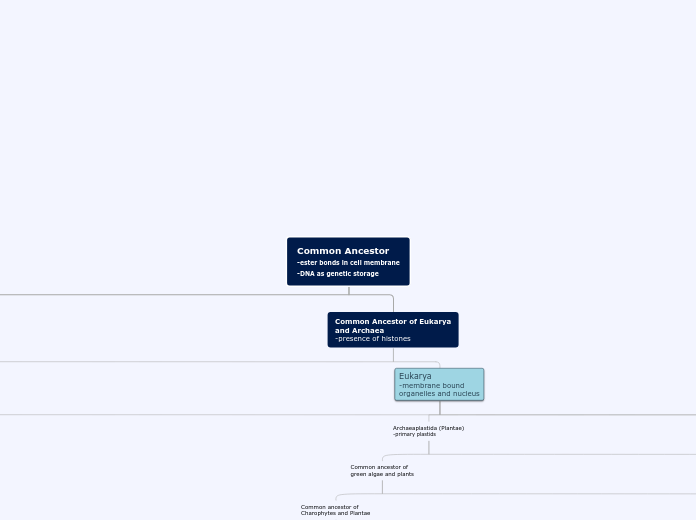
The text delves into the intricate world of genetics, highlighting its fundamental role in the diversity of life on Earth. It explores genetic variation and how it drives evolution through mechanisms such as gene flow, genetic drift, and natural selection.