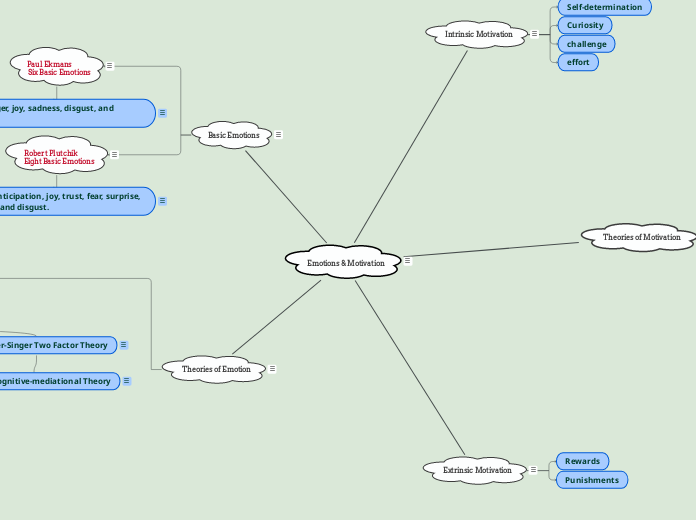
Emotions & Motivation
Emotions influence, change and motivate individuals.
Theories of Emotion
Theorists input about the physical effects of emotions and how they're connected.
James -Lange Theory
This theory suggests arousals, the physical effects than the emotion.
Cannon-Bard Theory
This theory suggests no arousals and straight to physical effects and emotion.
Schachter-Singer Two Factor Theory
This theory suggests arousal first, the physical effects with a cognitive label, then the emotion.
Lazarus' Cognitive-mediational Theory
Arousal leads to appraisal leads to fear/heart pounding and sweating.
Emotional Intelligence (EQ)
Emotional Intelligence is connected because knowing all the emotions and their combinations may help lead to better Emotional Intelligence.
Self Awareness
Self Regulation
Empathy
Skilled Relationship
Basic Emotions
The basic emotions are the fundamentals to emotion.
Robert Plutchik
Eight Basic Emotions
This theory lead to related emotions. With expanded emotions comes complex emotions.
anger, anticipation, joy, trust, fear, surprise, sadness and disgust.
The eight basic emotions.
Paul Ekmans
Six Basic Emotions
Universal facial expressions from the time you're born.
fear, anger, joy, sadness, disgust, and surprise
The six emotions by Paul Ekman.
Extrinsic Motivation
The need for praise and if it is not there then motivation may be different for the individual.
Punishments
Rewards
Theories of Motivation
Theories that further explain intrinsic and extrinsic motivation.
Evolutionary
Behaviourist
Cognitive
Humanistic
Add text
Evolutionary Understanding
of Motivation
At the primitive level, drive and need are tied to motivation for basic needs like food.
Need
Drive
Drive Theory
A further primate theory for an organism and its motivation.
Conflict
Competing motives where an individual must choose two or more competing motives, behaviours or impulses.
Three Types
of Conflict
The expansion of those conflicts.
Approach- approach
Fear of missing out is an example of this.
Avoidance- Avoidance
Fear of choosing two bad choices.
Approach-avoidance
Fear of doing something fun but will deter homework.
Homeostasis
Consistently being balanced and stable for needs.
Intrinsic Motivation
How an individual talks about themselves and how you use your words.
effort
challenge
Curiosity
Self-determination