REVISION ACTIVITIES
1. What is the difference between a bit and a byte?
2. What is the difference betweenhardware and software?
3. Classify these elements as computer hardware or software: CPU, Window 7, Ubuntu, RAM, bit, USB memory, hard drive,mouse, Internet Explorer, scanner, Mozilla Firefox.
4. Do the following conversions:
a) How many KB are in 2GB?
b) How many MB are there in 1TB?
c) How many bits are there in 1TB?
d) How many MB are there in 4096KB?
e) How many GB are there in 1012 bytes?
5. Name four peripheral input devices,four peripheral output devices and three peripheral input/output devices.
6. What is a microprocessor? What factors determine a microprocessor’s performance?
7. Write a list of all the types of memory that you know about and describe them.
8. What is the motherboard? Name some of its elements and describe their functions?
9. Write three lists of operating system, application programs and programming languages respectively, choosing from the following: Word, PowerPoint, Norton, Yahoo, Winamp,Visual Basic, Calc, Windows7, Chat, Mac OS, Paint, Writer, Linux, MSN, Excel,Logo.
Practice: SCRATCH (photocopies)
(Photocopy with the image, names )
If you open the outer case of a computer, you will see it.. All the parts of a computer are attached there directly or indirectly.
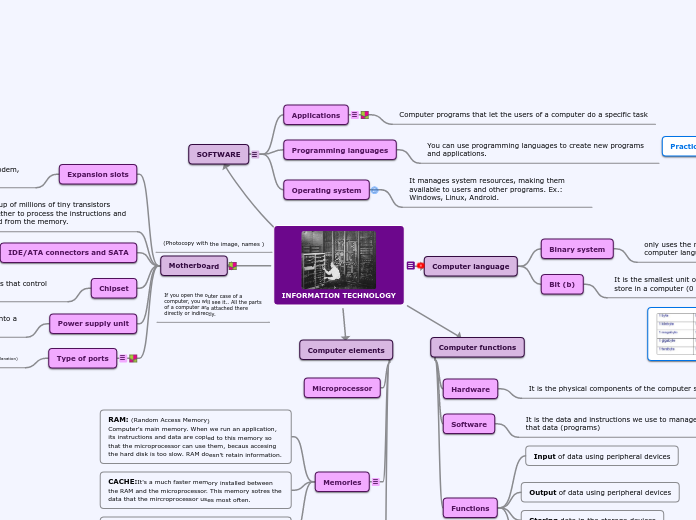
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY
You are going to watch a video about de history of computers. First, on your own, outline the principal ideas of it. Then, in groups, you are going to do a timeline about computers.
SOFTWARE
What are the differences between an operating system, an application and a programming language? Find out what operating systems are available nowadays.
Operating system
It manages system resources, making them available to users and other programs. Ex.: Windows, Linux, Android.
Programming languages
You can use programming languages to create new programs and applications.
Applications
Classify the following applications: Norton, Mozilla Firefox, Excel, Writer, The Sims, WinRAR, GIMP, Nero, Google Chrome
Computer programs that let the users of a computer do a specific task
Motherboard
Type of ports
Write down which ports we can connect the following devices to: mouse, keyboard, USB memory, monitor.
(Photocopy with the image, names and explanation)
Power supply unit
Transforms a 230V AC(alternating current) into a low voltaje DC (direct current)
Chipset
It is a group of integrated circuits that control the flow of information
IDE/ATA connectors and SATA
Link the hard drive, CD and DVD drives
Chips made up of millions of tiny transistors working together to process the instructions and data received from the memory.
Expansion slots
Allow us to add new conponent, such as a modem, sound card, network card or graphics card.
Computer elements
Units of storage
Name ten types of storage units and classify them according to wheter they are magnetic, optical or solid-state devices.
Solid-State memory (flash, cards, pen drives)
They store information using transistors acting as switches. We connect them to the computer through an USB port or other slots.
Optical discs (CD-ROMs, DVDs and Blue-Ray)
The disc drive emits a laser onto the disc and reflect off the flat areas. The lig signal is reflected back to an optical sensor that turns into a digital signal. Blue-Ray technology uses a special blue laser to store much more information.
Magnetic discs (Hard/external hard disks)
They store bits by positioning millions of tiny magnets. To access a piece of data, the disk spins around until the read head is above the area where that piece of data is stored.
Memories
- What is the function of a computer's BIOS? Do all computers have a BIOS? Explain why.
ROM-BIOS: When you turn on your computer, it automatically checks the system. If everything is correct, the BIOS starts the operating system.
CACHE:It's a much faster memory installed between the RAM and the microprocessor. This memory sotres the data that the mircroprocessor uses most often.
RAM: (Random Access Memory)
Computer's main memory. When we run an application, its instructions and data are copied to this memory so that the microprocessor can use them, becaus accesing the hard disk is too slow. RAM doesn't retain information.
Microprocessor
Computer functions
Functions
Processing data in the central procesing unit (CPU), using the microporcessor or memory
Storing data in the storage devices
Output of data using peripheral devices
Input of data using peripheral devices
Software
It is the data and instructions we use to manage that data (programs)
Hardware
It is the physical components of the computer system
Computer language
Bit (b)
It is the smallest unit of information that we can store in a computer (0 or 1)
Binary system
only uses the numbers 0 and 1. This is the computer language.