arabera raj gaz 8 years ago
715
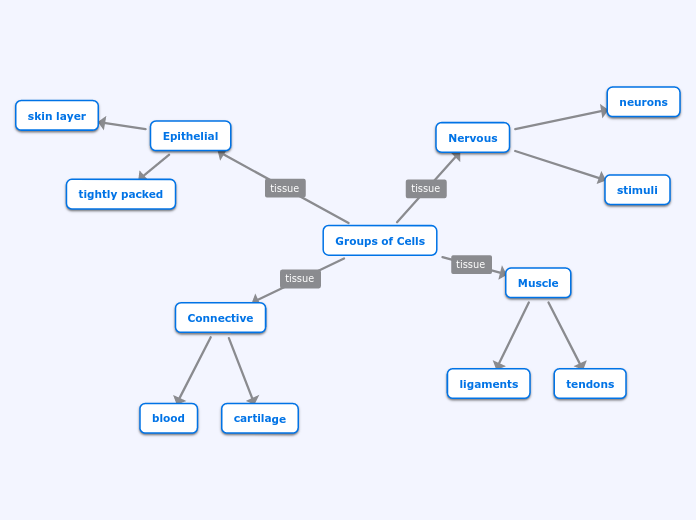
Hiearchy
Autoimmune diseases are characterized by the immune system mistakenly targeting and destroying the body’s own healthy tissues. Central to the body’s immune response are various components of the lymphatic and musculoskeletal systems.