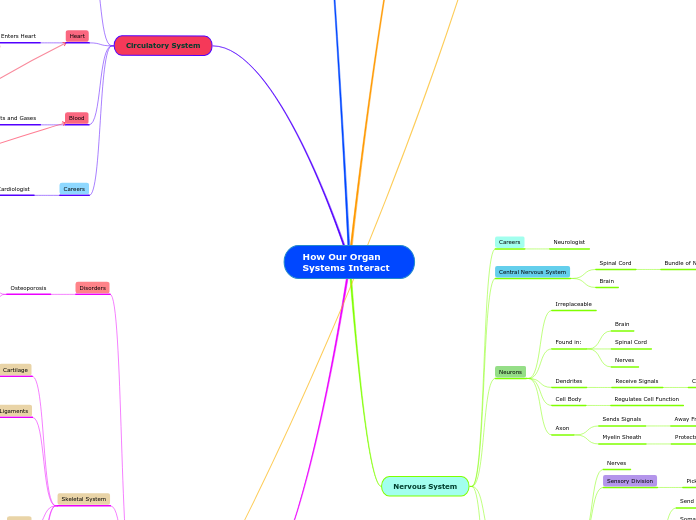
How Our Organ Systems Interact
Musculoskeletal System
Musculoskeletal Physician
Orthopedist
Muscle System
Skeletal Muscle
Bundles of Fibres
Multinucleated
Contracts and Relaxes
Allow us to Move
Smooth Muscle
Found In Organs
Move Substances Across Body
Example: Digestive Tract
Not Striated
One Nucleus
Cardiac Muscle
Gap Junctions
Contracts and Relaxes Simultaneously
Pumps Blood
Usually One Nucleus
Muscle Found in Heart
Striated
Allows For Movement
Skeletal System
Protects Our Organs
Supports Body
Bones
Two Types
Appendicular
Help us Move
Axial
Provide Skeletal Support
Example: Rib Cage, Skull, Etc
Minerals
Collagen
Cells
Hard and Dense
Bone Marrow
Yellow Bone Marrow
Stores Energy as Fat
Red Bone Marrow
Produces Blood Cells
Ligaments
Fibers of Collagen
Connect Bones Together
Allow Joints to Move
Tough and Elastic
Cartilage
Specialized Cells and Collagen
Provides Support Between Bones
Osteoporosis
Stooped Posture
Loss of Height
Back Pain
Zoledronic acid
Ibandronate
Risedronate
Alendronate
Circulatory System
Cardiologist
Blood
Transports Nutrients and Gases
Capillaries
Helps With Homeostasis
Take Carbon Dioxide
Deliver Oxygen
Tissue
Organs
Arteries
Carry Oxygenated Blood
Away From Heart
Veins
Carry De-oxygenated Blood
Towards Heart
Heart
De-oxygenated Blood Enters Heart
Blood Travels
Pulmonary Artery
To Lungs
Blood is Oxygenated
Re-Enters Heart
Travels to Aorta
Pumped Throughout Body
Delivered to Organs
Releases Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
Coronary Artery Disease
Discomfort in Arms and Shoulder
Shortness of Breath
Weakness
Chest Pain
Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery
Lifestyle Changes
Respiratory System
Oncologist
Respiratory Therapist
Cellular Respiration
Lungs
Diaphram
Air is Inhaled
Passes Through Pharynx
Enters Trachea
Bronchi
Bronchioles
Alveoli
Surrounded By Capillaries
Enters Alveolar Sac
Diffusion Occurs
Oxygen Enters Blood
Carbon Dioxide Enters Lungs
CO2 is Exhaled
Epiglottis Pointed Upwards
Allows
Air Entering Trachea
Pneumonia
Nausea and Vomiting
Rapid Breathing
Fever
Cough
Rest
Antibiotics
Lung Cancer
Chest Infections
Breathlessness
Persistent Cough
Coughing Blood
Radiotherapy
Chemotherapy
Immunotherapy
Nervous System
Alzheimer's Disease
Taking Longer to Complete Tasks
Poor Judgement
Memory Loss
Medication
Cholinesterase inhibitors
N-methyl D-aspartate
Namenda
Peripheral Nervous System
Motor Division
Autonomic
Parasympathetic Nervous System
Sympathetic Nervous System
Involuntary
Responsible for Involuntary Functions
Lungs Breathing
Heart Beating
Somatic
Voluntary
Controls Skeletal Movement
Arms, Legs, Etc
Send Directions From Brain
Sensory Division
Picks up Sensory Stimuli
Neurons
Axon
Myelin Sheath
Protects Axon
Sends Signals
Away From Cell Body
To Other Cells
Regulates Cell Function
Dendrites
Receive Signals
Convey Information
Cell Body
Found in:
Nerves
Irreplaceable
Central Nervous System
Brain
Spinal Cord
Bundle of Nerves
Connects Brain to Other Parts of Body
Neurologist
Digestive System
Disorders
Inflamatory Bowel Disease
Treatments
Immunomodulators
Corticosteroids
Amino salicylates
Surgery
Symptoms
Fatigue
Weight Loss
Abdominal Pain
Diarrhea
Food Enters Mouth
Saliva
Breakdown Biomolecules
Mechanical Digestion
Teeth
Physically Breaks Food
Tongue Forms Food Into Bolus
Bolus Gets Swallowed
Enters Esophagus
Peristalsis
Moves Food Down
Food Enters Stomach
Stomach
Sphincter
Prevents Backflow
Covered In Mucus
Acid Doesn't Penentrate
Chemical Digestion Occurs
Gastric Acid
HCL
Pepsin (Enzyme)
Results in Chyme
Chyme Enters Small Intestine
Small Intestine
Three Parts
Ileum
Jejunum
Duodenum
Chemical Digestion
Biochemicals
Enzymes
Released From Other Organs
Pancreas
Subtopic
Gallbladder
Moves Chyme
Absorption
Lining of Small Intestine
Villi
Microvilli
Absorb Nutrients
Transport Through Capillaries
Large Intestine
Feces
Bacteria
Undigested Contents
Reabsorbs Water
Contains Many Bacteria
Supplies Organs
Provides Energy
Covers Food
With Gastric Acid
Epiglottis in Closed Position
Prevents
Food Entering Trachea
Careers
Gastroenterologists