arabera KP - 10MS 863701 Jean Augustine SS 5 months ago
86
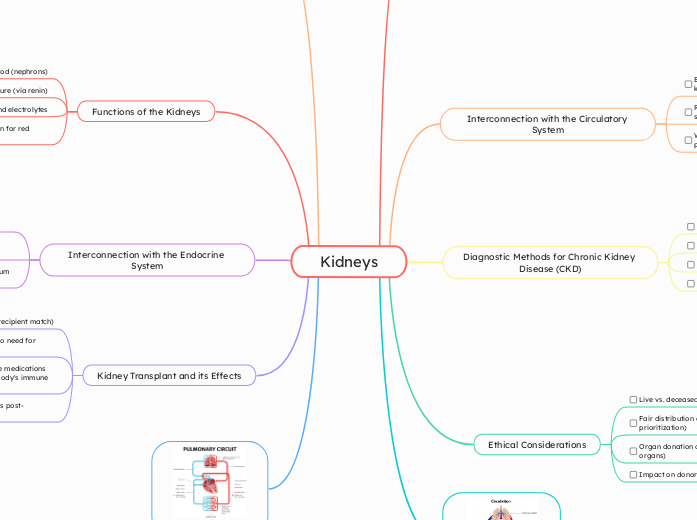
Kidneys
The kidneys play a crucial role in the body's homeostasis by interacting with the endocrine and circulatory systems. They regulate blood pressure through the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, produce erythropoietin to stimulate red blood cell production, and secrete calcitriol to maintain calcium balance.