METHODOLOGY AND THEORY OF LEARNING LANGUAGES
THEORIES OF LANGUAGE ACQUISITION
LANGUAGE ACQUISITION
Nativist Theories
Linguistic Universals
STRONG
Reflections specific in language
WEAK
Reflections universal in language
Language Acquisition Device (LAD)
Assess
Developing language system
Kind of linguistic system
Children is born with
Innate organizing principles
The concept of
“Sentence"
Innate knowledge
Linguistic universals
Certain type is possible
Other types are'nt
Refine
Syntactic systems
Phonological systems
Distinguish speech sounds
Language acquisition period
Two and twelve years
Ability innate to learn language
Biological endowment
Transformation capabilities
Categorization
Language emerges
During maturational process
Children
Word order occurs
During language acquisition
Acquire hierarchical grammar
Cannot establish longer sentences
Language is acquire
generalizations
approximations
reinforcent stimilu
operant learning
B. Frederic Skinner (1904-1990)
Specific linguistic behaviors acquire
Operant conditioning
Cognitive Theories
The child's temporal reference
Breaks free from the present moment
Another perspective.
Other moments and events
Imagining him/herself
Cognitive and mental development
Determinant the language acquisition
Segment expressions
In sounds and meanings
Retain Items
In long-term memory
In short-term memory
Active Process
Learner is'nt
Passive reactor
To external stimuli
Children is born
With some sort
Of process mechanism
Procedures and inference rules
Atheoretical Studies
Early steps
Short phrases
Few connections
pronunce two, three words
In one
Babbling
Seek communication
Before production
Being acquired
Linguistic ability
Linguistic knowledge
Nature
Speech development
Theory of language
Child language
Prevocalic stage
Toward
Clear speech
METHOD, METHODOLOGY, THEORIES, FIRST AND SECOND LANGUAGE ACQUISITION
Theories About First and Second Language Acquisition
THEORIES OF SECOND LANGUAGE ACQUISITIONS
Phychologycal Principles
The Humanistic Psychology Theory
Karl Ransom Rogers (1902-1987)
teachers ought to be
Get in touch and listen students
Consider people
Facilitator
Learners require
Excellent teachers
Their can help pupils learn
Any sort of information
Enviromental features
Considering in learning
Accustomed to such environmen
Environment
Concept of a person
Learner becomes consious
Their own knowledge
Effective operations
The Cognitive Learning Theory
Frank Smith (1921-2007)
Process of retention
Two types of memory
Long-term
The most significant is remembered
Short-term
Informtion by some seconds or minutes
Learning meaningful
If the person wants it
Depends of human
Motivations
Aspirations
Goals
Needs
Manufactoring meaningfulness
David Paul Ausubel (1918-2008)
Can learn by means
A meaningful procedure
Relates
What the person has acquired recently (rote learning)
Person alredy know (meaning learning)
The Neobehaviorism
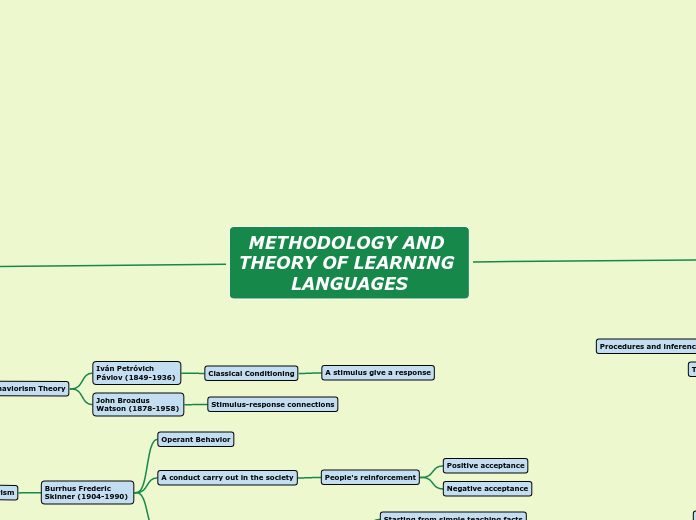
Burrhus Frederic Skinner (1904-1990)
Programed Instructiong
A special system
Finishing with difficult
Starting from simple teaching facts
A conduct carry out in the society
People's reinforcement
Negative acceptance
Positive acceptance
Operant Behavior
The Classical Behaviorism Theory
John Broadus Watson (1878-1958)
Stimulus-response connections
Iván Petróvich Pávlov (1849-1936)
Classical Conditioning
A stimulus give a response
THEORIES FIRST LANGUAGE ACQUISITION
Generative Theories
Theories
The Cognitive Approach
Important authors
Dan Isaac Slobin
The meaning of words and thing
The first thing
Humans acquire
Then get syntax
Jean William Fritz Piaget (1886-1980)
Language become
In terms of a interrelationship
With linguistic knowledge (devolop daily)
Lois Bloom
Children learn by
By underlying relationships
Child was born
A sort of knowledge
About first language
Human brain
Organaized in levels memory
Emotion
Meaning
Thought
Perception
The Nativist Approach
According
Larry B. McNeill (1951-2004)
Children can learn
Evaluation device
To use linguistic facts
Understand and choose
One linguistic information
Arrange linguistic data
For futher use
Recogize differents speech
Avram Noam Chomsky (1928-2017)
Children choose
Correct grammar rule
Children already have
A universal knowledge
Syntax and grammar
Childrens make
Their own rules
Use of language
Childrens are pro-programmed
To get first language
Enables to learn
Language spoken
Children learn through
Mechanism of innate language
Behavioristic Theories
Children not able to learn
All of the syntax patterns
At beginning of their lives
Is not rewards
Fist Language
Consciously learned
By means of oral stimulus
Is reinforced untill became a habit
They have a nature
Organize and provide
About some statements
Child get syntax patterns
On stimulus response
Supported by imitation
Basics Aspects About Language
TEACHING
Systematic process
Used by teachers
(or any person)
Learning process
LEARNING
Conscious process
Intensive repetition
Better understanding of new facts
Within the human brain
Acquisition
LANGUAGE
Establish communication or relationships
Composed of sounds
Are used in a specific culture
Organized system
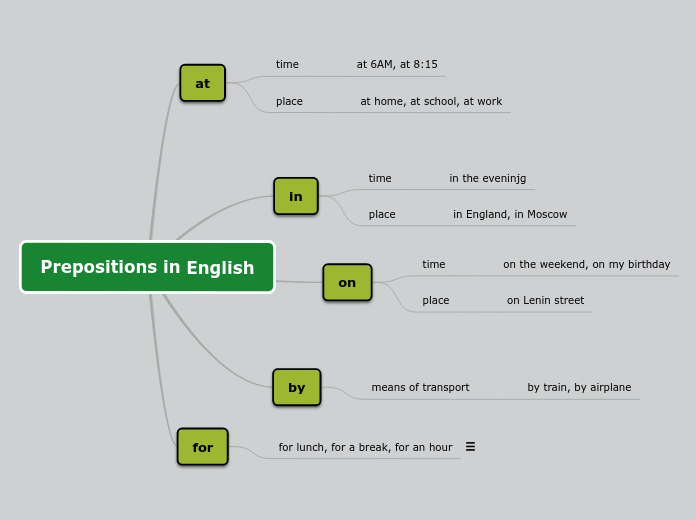
Method, Methodology Language Teaching
Methodology
Comes from Latin roots
LOGY/LOGIE = procedure or
system
METHODUS = way to
reach a goal
Procedures and activities
Are used
To teach
Target Language
Will be used to teach
Content of the syllabus
Method
Comes from Greek roots
HODOS = way
META = goal
Road or way
To reach a purpose
PROCEDURE
Role of some techniques
In learning/teaching process
Resources to develop, implement best practices
Additional elements in learning/teaching process
Equipment
Space
Time
Exercises and practical activities
To help students
Understand the new topics
Teaching and learning teqchniques
for inttroduce new topics in class
Final step
Teaching/leraning process
DESIGN
Describes
Instructional materials, types and functions
Basic in language teaching approach or method
Setting objectives
Reinforcent teaching
Teachers
Not necessary
Non-native language
Students can be prepared
Self-instruction
Direct student's learning
Become
Helps to acquire
The guide of students
Tarjet language
Facilitators
Learners
The approach and method
Always be based
Philosophy of the student
Needed to carry out
Educational process
Syllabus
The language assessment system
Teaching approach or method
Describes the connection
Learning
Language theories
APPROACH
Theories of the nature of language learning
Design - Procedure
Theories of the nature of language
Interactional
Subtopic
Functional
Means in order to state meaning
Semantical field of the language
Structural
Find the meaning
Grammar units and operations
Giving syntax of the language
Give some knowledge, theories
Nature of language