models of system development
Agile Development
Disadvantages
1. Hard to know at the beginning how hard it will be to deliver the product
2. Does not focus as much on design or documentation
3. If customer feedback is not clear or accurate, can derail the product
4. Needs experienced programmers to do this process
Advantages
1. High customer satisfaction
2. Focuses on the interactions between the customers and developers
3. Faster delivery of the product
4. Better attention to design and technical aspects
The first phase is called Concept. This is where the scope of the project and priorities are outlined. Cost, estimated time, project features, and requirements are also included in the outline.
In the next phase, Inception, a team is made, roles are set, and tools needed for the project are given out. Competitors' strengths and weaknesses are also discussed. This phase has 2 parts (UI/UX design and Product Architecture).
The third phase, Iteration, is the longest phase. The developers and designers make sure that all of the needs of the business are being met and the code is updated.
The base product is made and features are added to it as needed.
The fourth phase, Testing, is where the product is tested to find flaws and make sure the product works as intended and the code is the best it can be.
In phase five, Release, the product is delivered to the users. The product must meet the users' needs. Need to test the product and make sure it does not have any problems beforehand.
The last phase, Review, is where the customers give their feedback on the product so the makers know what to change, add, or update.
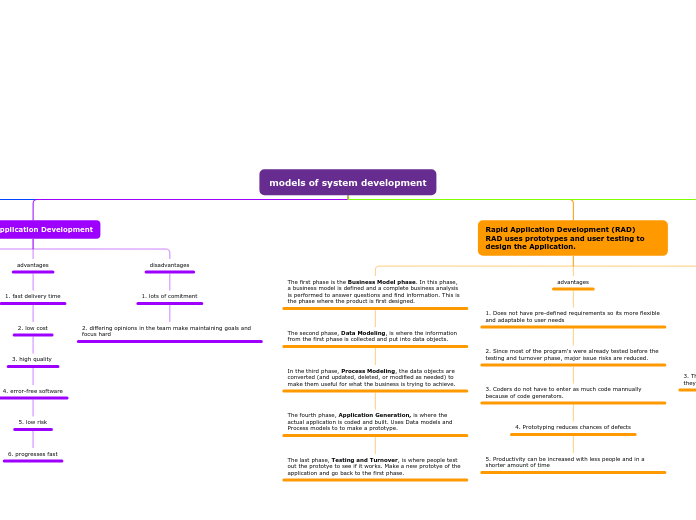
Rapid Application Development (RAD)
RAD uses prototypes and user testing to design the Application.
1. Can only be used for big projects
2. Can not use if for all applications
3. There is no documentation to show progress or problems so they are hard to keep track of
4. Needs more skilled developers to inpliment
1. Does not have pre-defined requirements so its more flexible and adaptable to user needs
2. Since most of the program's were already tested before the testing and turnover phase, major issue risks are reduced.
3. Coders do not have to enter as much code mannually because of code generators.
4. Prototyping reduces chances of defects
5. Productivity can be increased with less people and in a shorter amount of time
The first phase is the Business Model phase. In this phase, a business model is defined and a complete business analysis is performed to answer questions and find information. This is the phase where the product is first designed.
The second phase, Data Modeling, is where the information from the first phase is collected and put into data objects.
In the third phase, Process Modeling, the data objects are converted (and updated, deleted, or modified as needed) to make them useful for what the business is trying to achieve.
The fourth phase, Application Generation, is where the actual application is coded and built. Uses Data models and Process models to to make a prototype.
The last phase, Testing and Turnover, is where people test out the prototye to see if it works. Make a new prototye of the application and go back to the first phase.
Joint Application Development
1. lots of comitment
2. differing opinions in the team make maintaining goals and focus hard
1. fast delivery time
2. low cost
3. high quality
4. error-free software
5. low risk
6. progresses fast
The first phase of the JAD is called Define Objectives. This is where the application's objectives are defined and all the things need for the project
The second phase is called Session Prepatation. Useful data, that is needed for the the session, is prepared.
The third phase, Session Conduct, is where a session is held and the major issued that need fixed are identified.
Documentation is the fourth phase. Once the product is made, documentation (and records) are shown in a meeting for the stakeholders to approve.
System Development Life Cycle
disadvantages
1. costs can raise if planning is not done right
2. Bugs can take time to fix (possible to miss deadlines)
advantages
1. Not very costly
2.Time efficient
3. improves cooperation between team members
4. low risk
Process
The first phase is the planning phase. This phase is where the project team is made. This is also the phase where feasibility studies are completed. Because of this, the phase is also called the Feasibility phase.
The second phase is the Analysis Phase. In this phase, the team finds out what each system needs to work on and evaluates the current system (advantages, disadvantages, and features).
The third phase is the Design Phase. The team defines what the system will do and how it will do it. They find all possible solutions and pick the one they think is the best.
The fourth phase is the Implementation and Testing Phase. This is the phase where the system is coded, installed, and tested. In this phase, all users are trained on how to operate the system.
The last phase is the Maintenance Phase and it is in this phase that people make sure the system is meeting all of the needs of the business and update the system if any security holes/bugs are found. It is in this phase that new features, updates, and backups are installed.