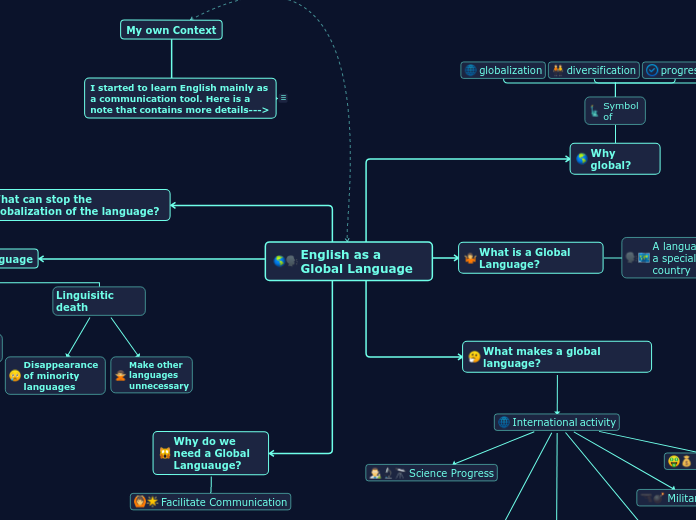
New 21st Century Skills
Partnership for 21st Century Skills
Life and Career Skills
Leadership and Responsibility
Productivity and Accounability
Social and Cross-Cultural Skills
Initiative and Self-Direction
Flexibility and Adapability
Information, Media and Technology Skills
ICT (Information, Communications and Technology) Literacy
Media Literacy
Learning and Innovation Skills
Communication and Collaboration
Critical Thinking and Problem Solving
Creativity and Innovation
Themes
Environmental Literacy
Health Literacy
Civic Literacy
Financial, Economic, Business and Entrepreneurial Literacy
Global Awareness
enGauge/Metiri
High Productivity & Quality, State-of-the-Art Results
Abilty to Produce Relevant, High-Quality Products
Intellectual, informational, or material products that serve authentic purposes and occur as a result of students using real-world tools to solve or communicate about real-world problems. These products include persuasive communications in any media (print, video, the Web, verbal presentation), synthesis of resources into more useable forms (databases, graphics, simulations), or refinement of questions that build upon what is known to advance one’s own and others’ understanding
Effective use of real-world tools
Effective use of these tools – the hardware, software, networking, and peripheral devices used by Information Technology (IT) workers to accomplish 21st century work – means using these tools to communicate, collaborate, solve problems, and accomplish tasks
Prioritizing, Planning, and Managing for Results
The ability to organize to efficiently achieve the goals of a specific project or problem
Digital Age Literacy
Global awareness
The recognition and understanding of interrelationships among international organizations, nation-states, public and private economic entities, socio-cultural groups, and individuals across the globe
Multicultural Literacy
The ability to understand and appreciate the similarities and differences in the customs, values, and beliefs of one’s own culture and the cultures of others
Information Literacy
The ability to evaluate information across a range of media; recognize when information is needed; locate, synthesize, and use information effectively; and accomplish these functions using technology, communication networks, and electronic resources
Visual Literacy
The ability to interpret, use, appreciate, and create images and video using both conventional and 21st century media in ways that advance thinking, decision-making, communication, and learning
Technological Literacy
Knowledge about what technology is, how it works, what purposes it can serve, and how it can be used efficiently and effectively to achieve specific goals
Economic Literacy
The ability to identify economic problems, alternatives, costs, and benefits; analyze the incentives at work in economic situations; examine the consequences of changes in economic conditions and public policies; collect and organize economic evidence; and weigh costs against benefits
Scientific Literacy
Knowledge and understanding of the scientific concepts and processes required for personal decision-making, participation in civic and cultural affairs, and economic productivity
Basic Literacy
Language proficiency (in English) and numeracy at levels necessary to function on the job and in society to achieve one’s goals, and develop one’s knowledge and potential in this Digital Age.
Inventive Thinking
Higher-order Thinking and Sound Reasoning
Include the cognitive processes of analysis, comparison, inference/interpretation, evaluation, and synthesis applied to a range of academic domains and problem-solving contexts
Risk-Taking
The willingness to make mistakes, advocate unconventional or unpopular positions, or tackle extremely challenging problems without obvious solutions, such that one’s personal growth, integrity, or accomplishments are enhanced
Creativity
The act of bringing something into existence that is genuinely new and original, whether personally (original only to the individual) or culturally (where the work adds significantly to a domain of culture as recognized by experts)
Curiousity
The desire to know or a spark of interest that leads to inquiry
Self-Direction
The ability to set goals related to learning, plan for the achievement of those goals, independently manage time and effort, and independently assess the quality of learning and any products that result from the learning experience
Adapabilty / Managing Complexity
The ability to modify one’s thinking, attitude, or behavior to be better suited to current or future environments, as well as the ability to handle multiple goals, tasks, and inputs, while understanding and adhering to constraints of time, resources, and systems (e.g., organizational, technological)
Effective Communication
Interactive communication
The generation of meaning through exchanges using a range of contemporary tools, transmissions, and processes
Social and Civic Responsibility
The ability to manage technology and govern its use in a way that promotes public good and protects society, the environment, and democratic ideals
Personal responsibilty
Depth and currency of knowledge about legal and ethical issues related to technology, combined with one’s ability to apply this knowledge to achieve balance, integrity, and quality of life as a citizen, a family and community member, a learner, and a worker
Interpersonal skills
The ability to read and manage the emotions, motivations, and behaviors of oneself and others during social interactions or in a social-interactive context
Teaming and Collaboration
Cooperative interaction between two or more individuals working together to solve problems, create novel products, or learn and master content