arabera lucas shen 1 year ago
444
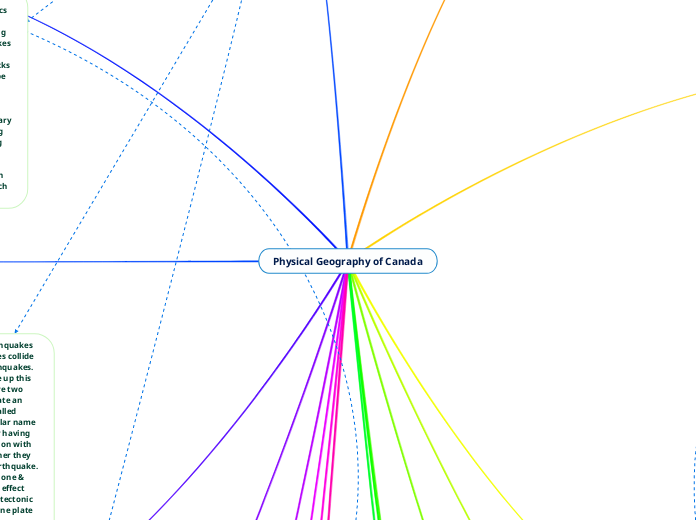
Physical Geography of Canada
The interaction between convergent tectonic plates leads to most earthquakes, especially when plates either push together or meet head-on, causing them to crumble or one to rise above the other.